NAB has just announced the launch of a new income offer, NAB Subordinated Notes 2, with the primary purpose of repaying NAB Subordinated Notes (NABHB), which are due to mature this year.
The Notes will pay a quarterly coupon of 2.2%-2.3% (margin determined by the book build) over the 90-day bank bill swap rate (BBSW), which was 1.77% at 10 February 2017. The initial indicative rate will be 3.97%-4.07% pa with the rate set on the date of issue. The Notes are expected to redeem on 20 September 2023 (subject to mandatory conditions not being breached) and will be tradable on the ASX under code NABPE.

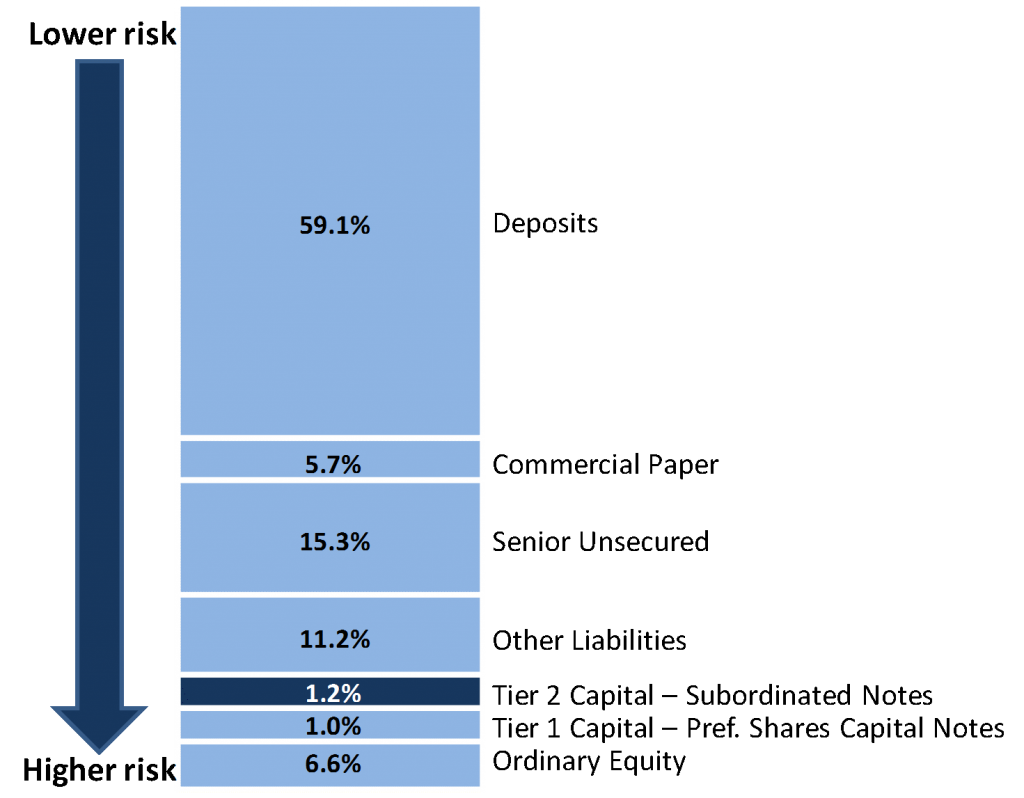
Subordinated notes
A key consideration in this issue versus last year’s hybrid or preference share issues from CBA, NAB and Westpac that offered margins of 4.9%-5.2% over BBSW is that NABPE is a subordinated note and will be treated as Tier 2 Capital. The reduced margin reflects the lower risk of these securities and offers investors another risk choice. This is more akin to a debt instrument, and unlike the listed bank capital notes and preference shares, distributions are non-discretionary.
Comparable securities
While there are a handful of listed subordinated notes (ANZHA, WBCHA, WBCHB and NABHB), Westpac Capital Notes 2 remains the only listed issue containing a non-viability clause (explained later) and offers the closest comparison.
Due to the short term to maturity of the existing Tier 2 subordinated notes, investors should also consider the unlisted institutional market when looking at relative pricing.
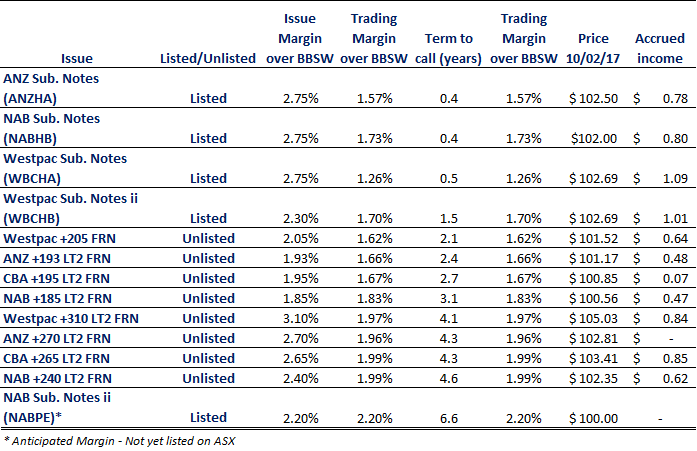
Arguably, the closest comparable in the unlisted market is NAB’s Tier 2 Floating Rate Notes expected to be repaid in 2021 (NAB +240 LT2 FRN above).
Our view on NAB Subordinated Notes 2
We find that retail investors are often looking to hybrids as an alternative to cash accounts rather than equities. The fall in cash rates to historical lows means investors are forced to look elsewhere than term deposits or cash accounts for income and hybrids have been a natural beneficiary.
However, subordinated notes are often overlooked as their perceived risk among direct investors is equal to preference shares and capital notes. This likely explains the wider margins we often see in the listed subordinated notes vs the unlisted market.
Our view is that they can offer value as an alternative to investor portfolios. The greater security, lower volatility and increased certainty of income distributions means they are attractive to those willing to take more risk than government bonds yielding below 2% pa and term deposits yielding anywhere between 2%-2.5% pa, but less volatility than the listed hybrids. In a world where rates look like they may be on the rise, floating rate notes can offer value to investors seeking income.
Equity pundits will often point to equities providing both income and capital growth, but for investors who can’t stomach the equity roller coaster, subordinated notes offer a lower risk alternative to equities, preference shares and capital notes.
Pricing NAB Subordinated Notes 2
At first glance, the Margin to Maturity of both listed and unlisted subordinated notes indicates that NAB’s anticipated margin of 2.2% over BBSW is priced in line with the secondary market. However, the listed market typically trades at wider premiums than the institutional market and we would prefer a wider margin. In addition, the new NAB issue includes some updated APRA-required write-off clauses which make it rank junior to other Tier 2 issues by NAB.
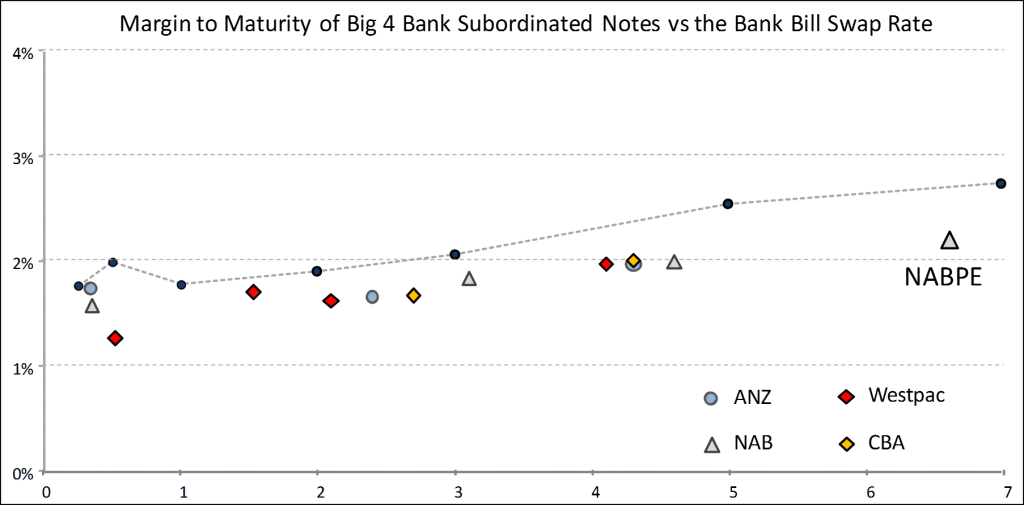
Note: Investors in subordinated notes earn the sum of the margin and BBSW.
The pricing reality is that NAB does not need to pay over the odds and the bank is not looking to raise large swathes of new money. The majority of this issue is expected to be acquired by existing investors rolling from NABHB and the lack of longer term ASX-listed subordinated notes means the demand will be strong.
Overall, it’s an opportunity for investors to diversify into lower risk listed securities that offer greater capital stability than hybrids. Do not feel neglected if you do not secure an allocation, and investors should note the anticipated repayment of ANZHA and WBCHA in mid-2017 is likely to result in further issuance in the near future.
Note there is automatic conversion under the Non-Viability Trigger Event (explained below) and income is unfranked. Investors often overlook that returns quoted on some hybrids include franking credits. Unfranked payments should be considered more attractive, avoiding the need to wait until the end of the tax year to claim back the franking.
Non-Viability and Inability Event clauses
Investors who are familiar with the new style hybrids seen over the last couple of years will be aware of the new clauses. They are a result of APRA requiring further reassurance that in another GFC event, if required, some securities such as hybrids would convert to ordinary equity, thereby reducing the bank’s debt costs and protecting deposit holders.
Now that banks have to hold a higher level of subordinated debt and a better-quality loan book, it seems unlikely that these conditions will be breached, however, investors would do well to consider the increased disclosure and warnings within each prospectus over the last couple of years.
Newer style subordinated notes contain a Non-Viability Trigger Event that is subject to rulings by APRA that have yet to be tested. In theory, should APRA view the bank as non-viable without a capital injection, the subordinated notes and Tier 1 hybrids would automatically convert to ordinary shares. Tier 1 hybrids would convert prior to Tier 2 subordinated notes, and there may be junior categories within the subordinated notes issues.
We have also seen a gradual introduction of an Inability Event Clause which states that in the event that the issuer is unable to issue further ordinary shares (ie the company has ceased trading), note holders lose their investment. Investors would do well to remember this is an additional risk.
NAB Subordinated Notes 2 will be listed on the ASX and the price will be subject to market movements. Investors selling on market may receive a price lower or higher than the issue price.
Sulieman Ravell is Managing Director at Wealth Focus, and publishes the FundsFocus newsletter This article is general in nature and it does not take into account your needs, objectives or financial situation. You should always take these matters into consideration before making an investment decision.