Biotechnology and specialty pharmaceutical shares were key drivers of the post-GFC recovery in equity markets, but their stellar run came to an end in September 2015 when drug pricing and affordability were thrust into the spotlight.
Stock shocks in global healthcare
Hillary Clinton famously accused Turing Pharmaceuticals on Twitter of ‘outrageous’ price gouging following its decision to raise prices of a 62-year-old drug (Daraprim) to $750 per tablet from $13.50. Her comments sparked a sell-off in biotechnology and specialty pharmaceutical shares. Drug pricing is now an election campaign issue in the US, with some candidates talking of price regulation.
During the same period, the dubious business practices of specialty drug-maker Valeant Pharmaceuticals came under intense public scrutiny, leading to a congressional investigation; Valeant shares have more than halved since. In response, pharmaceutical executives argue that price hikes are rarely realised in full by the manufacturer (with the majority given away through rebates) and reflect the high risk, high costs and long timeframes associated with developing new drugs.
Australian stocks have done better
Interestingly Australian healthcare shares did not react to the same issues (as seen in the chart below), and were driven by more stock-specific factors.
With a large proportion of their earnings derived offshore, the weaker AUD has benefitted domestic healthcare companies. In addition, more money has flowed into the domestic sector, given it is one of the few remaining pockets of growth in our share market. As a result, the domestic sector currently trades at historically high valuations versus offshore peers. However, given Australian healthcare companies face many of the same risks as their international peers, there are arguably better opportunities to invest offshore.
Australian healthcare stocks outperformed global peers
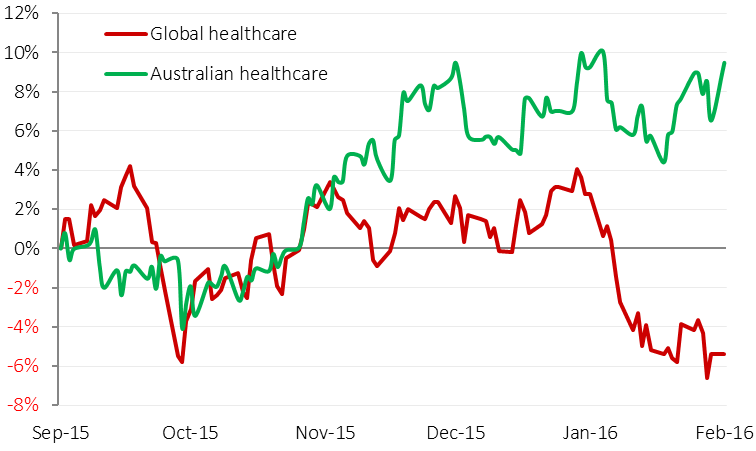
Source: Bloomberg
Falling off the patent cliff?
The ‘patent cliff’ refers to a period between 2003 and 2013, when drug patents that protected many of the highest selling drugs in history from competition expired. The industry reacted by undertaking a wave of M&A deals while also increasing investment in lower risk drug development (such as ‘biologics’, see below) to diversify their earnings. A period of recovery and improved R&D productivity ensued.
A more subtle driver of the previous cycle was a decline in R&D productivity, which has improved since then through higher investments in lower-risk drug development. The chart below shows that the probability of success in developing new ‘small molecule’ drugs was in clear decline between 2003 and 2011, meaning companies had to conduct more trials with more drug candidates to gain approval. Recent data shows a reversal of this trend from 2010 to 2014, coinciding with a recovery in pharmaceutical valuations.
Percent of preclinical drugs ultimately approved

Source: KMR, Bernstein
Why is ‘biologics’ more promising?
In our view, the more relevant and striking driver of productivity improvement has been the development of a new drug class called biologics. Biologics are commercial products derived from biotechnology, manufactured in a living system such as a microorganism, a plant or an animal.
Data on approval rates shows that biologics carry a dramatically higher likelihood of success in being developed compared to small molecule drugs, and so those companies developing more biologic drugs are more likely to have a greater number of successful products. Small molecule drugs are synthetically produced chemicals where the drug chemistry and structure is known, but often carry less favourable side effects. Biologics on the other hand are treatments made by manipulating naturally occurring systems. Because they mimic naturally occurring pathways in the body and are typically composed of either sugars, proteins, DNA or living tissues, they tend to have less off-target effects with outcomes that are more predictable.
Approval rate for small molecule vs. biologic drugs (%)

Source: KMR, Bernstein
Our focus in looking for suitable investments is on diversified pharmaceutical shares with breadth in treatments for more favourable diseases and weighted to biologics – such as Merck & Co. We will avoid shares that have exposure to the pricing issues highlighted earlier including generic competition – diabetes as an example strikes us as a market that will come under intense pricing and competitive pressures from generics.
Justin Braitling is a portfolio manager at Watermark Funds Management. This article is for educational purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. For more details on the global healthcare sector, see www.wfunds.com.au.