In April 2019, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) released its third report on marketplace lending, the Survey of marketplace lending providers: 2017–18. The report paints a clear picture of a once-nascent industry enjoying growth with new borrowing increasing by nearly 45% in the 2017-18 financial year. The report notes that this growth is moderating compared to the near doubling in funds borrowed the previous year (from $156 million to $300 million). By contrast, the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) reports that overall personal lending has declined by an astonishing 24% in the 12 months to March 2019.
ASIC’s report draws on a survey of 13 marketplace lenders, covering questions such as how investors and borrowers are matched, how credit risk and interest rates are determined and the characteristics of the loans funded, including amounts, term, security and default.
Five key findings in the report are:
1. More borrowers and investors are choosing marketplace lending
ASIC found that the number of retail investors on 1 July 2018 was 79% higher than in the previous year and had quadrupled since 1 July 2016.
While the rate of new investor growth was lower compared with the 2016-17 financial year, the total amount invested had increased by $108 million. At the same time, demand from borrowers rose from $300 million in the 2016–17 financial year to $433 million in the 2017–18 financial year, as shown below:
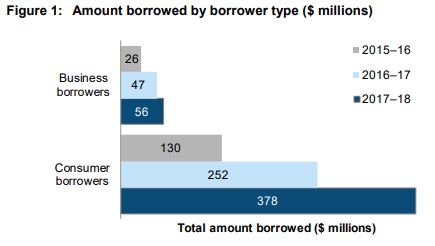
There are three main reasons for this growth.
First, the consistent returns offered by fixed income investments, such as consumer loans, make them an attractive alternative to more volatile products, such as shares. As investors seek to diversify, consumer loans build financial stability into diversified portfolios.
Second, after the revelations of the Royal Commission into Misconduct in the Banking, Superannuation and Financial Services Industry, consumers have become more alert to the issues associated with traditional finance providers and have been more willing to adopt newer business models and brands.
Third, consumers are more aware of the dangers of credit card debt and are seeking cost-effective solutions. APRA found that total personal credit card debt owed to banks declined by 4.8% in the year to March 2019, the second largest annual decline since 2002. More Australians are turning to the comparatively affordable interest rates associated with consumer loans.
2. Marketplace lenders are exploring new markets
Marketplace lending business models are evolving, with several platforms entering into new territory since the previous ASIC survey. The survey found that one retail platform established a separate platform for wholesale loans to fund specific types of loans, another platform moved investors to funding whole loans rather than fractions of each loan, whilst three platforms had started offering loans originated by third parties.
The report references RateSetter's renewable energy marketplace which provides loans for the purchase and installation of clean energy products, such as solar panels and home batteries. These markets allowed us to become the official administrator of the South Australian Home Battery Scheme and offers competitive loans supported by the Clean Energy Finance Corporation.
3. Interest rates have remained competitive
The ASIC report found that the average interest rate charged for marketplace loans entered into during the 2017–18 financial year was 11.5%, up from 10.5% in the 2016–17 financial year.
The average interest rate has not moved significantly since the first survey at the end of the 2015–16 financial year. With 71% of loans in the 2017–18 financial year attracting interest rates of 12% or less, this indicates that marketplace loans are generally offered at lower rates than those offered by more traditional institutions to this part of the market.
The figure below from the report shows the range of interest rates by borrower type.
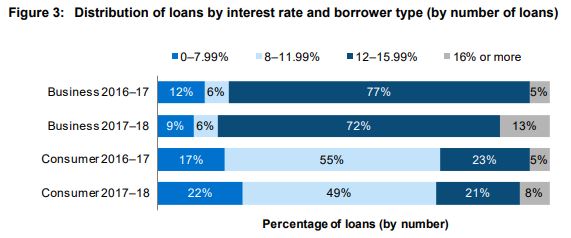
4. Security remains a priority
Five lending providers identified incidents of fraud, suspected fraud or cyber crime. While Corporations Act breaches were down from 10 to two suspected breaches, application fraud or suspected incidents of fraud increased from 353 to 545. Only one provider identified a cyber security incident.
All financial institutions must commit to robust security protocols including encryption processes (such as SSL Certificates) to secure data against misuse, interference and loss, unauthorised access, disclosure and modification.
5. The default rate has increased slightly
According to the report, ‘the average default rate for the 2017–18 financial year, weighted by dollar amount, was 2.9%, representing an increase of 0.7 percentage points on the 2016–17 financial year. Meanwhile, default rates varied across providers from 0 to 7% for consumer loans, compared to 0 to 3.4% in the 2016–17 financial year."
Although most marketplace lenders had fewer than 1% of loans in default, the risk of losing principal or interest owed in a more uncertain economic environment may drive investors towards platforms that have implemented models that provide additional measures to protect investors, such as RateSetter’s model where investors benefit from its Provision Fund.
Looking ahead
ASIC's survey shows that marketplace lending has now established itself as a credible alternative for investing and borrowing in Australia. The industry should continue to ride the wave of consumers looking for transparent, value-oriented products and continue to take market share from traditional financial institutions.
With the three largest marketplace lenders accounting for 86% of outstanding loans, similar to prior years, it also seems the industry make-up is now established.
Daniel Foggo is CEO of RateSetter, Australia’s largest peer-to-peer lender, and a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. Investors should make their own independent enquiries and consult with a financial adviser.
For more articles and papers from RateSetter, please click here.