During a span of just 21 days in January 2022, the rapid pace of change in the media and entertainment industry inspired three blockbuster deals.
Microsoft announced its intention to buy video game publisher Activision Blizzard for US$75 billion, a transaction that aims to bring the iconic Call of Duty and World of Warcraft franchises under the tech giant’s umbrella. Take-Two Interactive unveiled its plan to shell out US$12.7 billion for mobile game maker Zynga, best known for the FarmVille franchise. And Sony agreed to purchase Bungie, creator of the popular Halo and Destiny games, for US$3.6 billion.
If all three deals close, that’s US$85 billion of M&A activity centred on video games, the fastest growing segment of the media sector. The Activision deal is Microsoft’s largest acquisition ever and could vault it to the top of the US$200 billion gaming industry, just behind China’s Tencent.
Gaming’s global appeal fuels industry leaders in Asia and the US
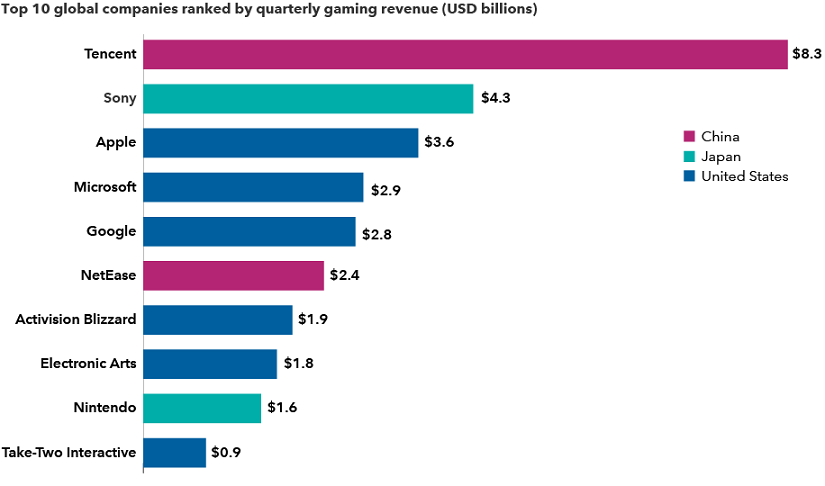
Sources: Capital Group, Newzoo. Quarterly revenue figures are estimates by research firm Newzoo, as at 30 September 2021.
Driven in part by a pandemic-era gaming boom, the fast-changing media landscape is fundamentally transforming the way people interact and entertain themselves in a world where traditional TV viewing and movie attendance are in serious decline. That dynamic makes interactive games even more valuable to the likes of Microsoft, Sony and others. Portfolio Manager Martin Romo says:
“I think it’s a testament to how powerful and alluring video games have become. The global gaming industry provides compelling entertainment at a reasonable cost and it’s already surpassed the movie industry in terms of annual gross revenue. Fundamentally, I think that growth is likely to continue and even accelerate in the years ahead.”
Streaming and social media competition heat up
The disruption extends to other areas of the media world, as well. Jody Jonsson, a Capital Group Portfolio Manager, says:
“Another big theme playing out here is that you have a lot of companies trying to get into each other’s business. There was a time when they had these sandboxes all to themselves, but that’s changing. Everyone is looking at everyone else’s sandbox and trying to jump in.”
For example, Netflix - the clear leader in streaming video - is encountering fierce competition from Amazon and Apple, as well as old guard media companies such as Disney. In less than three years, Disney’s streaming service, Disney+, has grown to 130 million subscribers.
In the social media space, TikTok is challenging Facebook parent Meta Platforms, attracting hordes of young viewers thanks to the power of its short-form videos. Facebook has responded by launching its own short-form video offering, dubbed 'Reels', which is growing in popularity, just not as fast as TikTok, which was the most downloaded app of 2021.
Other battles in the media business were lost years ago. For instance, a precipitous decline in traditional TV viewership - especially among young people - raises the possibility that cable TV packages, once a must-have in the US, may no longer exist in a few years. If live sports and news programmes ever move en masse to streaming services, that could spell the end of cable TV in its current form.
Young people are increasingly shunning pay TV in the US
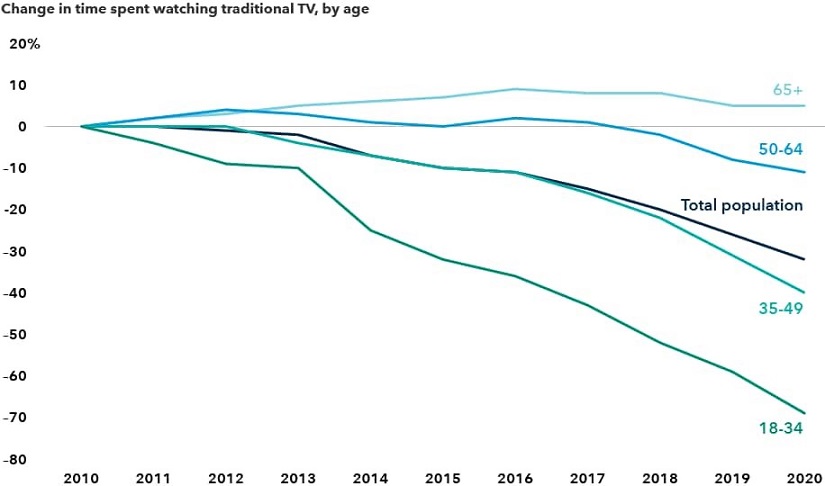
Sources: Capital Group, Nielsen. Traditional TV includes live TV and recordings of live TV (for example, using a DVR).
There’s no business like show business
This type of momentous change and disruption may appear surprising to some, but it’s par for the course in the media and entertainment biz, explains Capital Group equity analyst Brad Barrett, who has covered the industry for two decades:
“Media is always being roiled by technological change. It felt like a huge amount of change when the internet started disrupting traditional media outlets in the early 2000s. It felt huge when YouTube burst onto the scene. And then came social networking, smartphones and video streaming. They all caused a great deal of disruption and continue to do so.”
A new trend is the globalisation of content production and consumption. Case in point: Three of Netflix’s most popular series - Squid Game, Lupin and Money Heist - are filmed in South Korea, France and Spain, respectively. And they come with English subtitles, which had previously been a deterrent for many native-English speaking viewers. Not so anymore. Consumers are watching content from all over the world and English speakers embrace these non-English shows with enthusiasm. It’s a breakthrough for global creativity.
Metaverse now?
Looking ahead, what will be the next source of media disruption?
Based on the rising number of sensationalist headlines, the metaverse is certainly one candidate. Depending on who you ask, the much touted metaverse is either the future of the internet or a virtual reality pipe dream.
As technologists have described it, the metaverse is an incredibly immersive and expansive digital world in which people can interact, transact, play games, attend concerts, watch movies, meet co-workers in a virtual office and engage in myriad other activities through user-created avatars.
The idea is so powerful it prompted Facebook to change its name to Meta Platforms, promising to transform the social media giant into a 'metaverse company'. It will have plenty of competition, however. Microsoft declared the Activision deal is, in part, driven by a desire to develop compelling content for the metaverse, a world where virtual reality headsets may become as common as smartphones.
There are also many independent websites with a metaverse focus, including Sandbox, founded in 2012, and Decentraland, launched three years later. Users of these sites are already buying virtual land, virtual houses and virtual artwork, often with cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano and Solana.
The term metaverse was originally coined by Neal Stephenson in his 1992 novel Snow Crash. The concept was further popularised by Ernest Cline in his 2011 sci-fi novel Ready Player One, which was subsequently turned into a movie. One oft-cited answer when people ask, “What is the metaverse?” is to read Ready Player One or at least watch the movie.
Clearly, the concept has been around a while and it’s not all hype, says Peter Eliot, a Portfolio Manager:
“When I ask friends what they think of virtual reality, very few have tried it. That’s going to change fast, and it means the race is on for investors to appreciate and understand the metaverse. There’s already a lot happening, and it’s growing exponentially. I don’t think this is 10 years away. It’s more like metaverse now.”
Bandwidth needs are expected to soar amid the growth of the metaverse
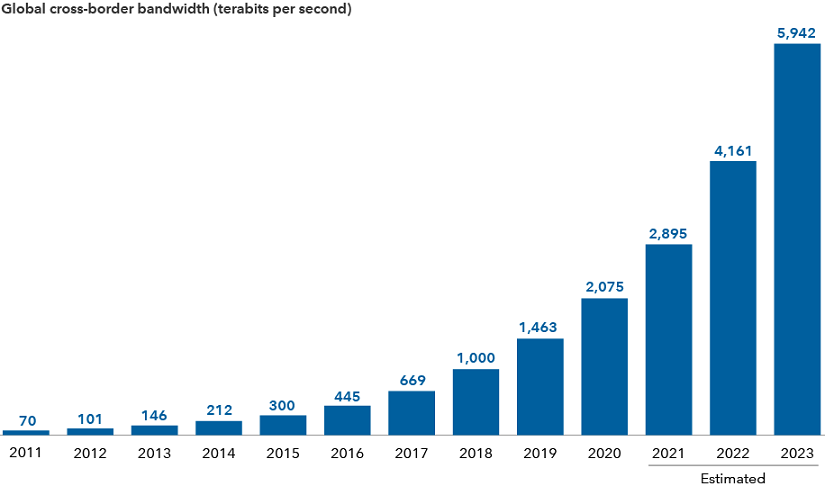
Sources: Capital Group, TeleGeography. Actual data through 2020. 2021 to 2023 are estimates.
Jody Jonsson and Martin Romo are Equity Portfolio Managers at Capital Group, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is neither an offer nor a solicitation to buy or sell any securities or to provide any investment service. The information is of a general nature and does not take into account your objectives, financial situation or needs. Before acting on any of the information you should consider its appropriateness, having regard to your own objectives, financial situation and needs.
For more articles and papers from Capital Group, click here.