This paper discusses current themes in the electric utility sector, specifically in decarbonisation, energy efficiency and energy storage.
Are renewables cost competitive?
The cost of onshore wind energy declined by 65% between 1988 and 2014 (according to the International Renewable Energy Agency) due to economies of scale, technology innovations and operational and maintenance improvements. Onshore wind can compete with fossil fuels, with the levelised cost of onshore wind estimated to be below €0.05 per kilowatt hour (kWh) versus coal at €0.049 / kWh and gas at €0.041 / kWh.
The expectation is that wind will continue to get cheaper as better siting, longer blades and taller towers drive productivity gains. In the UK, load factors have risen from around 34% in 2003 to around 45% in 2014. This is set to increase due to the high levels of R&D now being spent in an industry that has gone from a standing start to having key global turbine manufacturers such as Siemens, General Electric and Vestas.
Are renewables growing as part of the energy mix?
Renewable capacity additions represented about half the world’s total capacity additions in 2014, supported by:
(1) country and state decarbonisation targets eg US renewable portfolio standards (RPS) and EU carbon targets
(2) carbon taxes and UK carbon floor
(3) tax incentives eg US production tax credits and investment tax credits
(4) the social implications of burning fossil fuels such as smog, and
(5) reduced fossil fuel subsidies in countries including India, Indonesia and Spain.
We expect renewables will represent a growing portion of new generation capacity in the future, due to the above points and a lack of economically viable clean coal plants.
Is energy storage a game changer?
In short, yes. Effective energy storage can help back up intermittent renewable power and be used to power electric vehicles. Similar to renewables, the level of investment into lithium ion storage has seen prices decline dramatically. Tesla’s Gigafactory is currently producing batteries at US$190 per kWh, with an expectation of 30% reduction coming from economies of scale, reduction of waste, a closer supply chain, vertical integration and process optimisation.
Much as RPS targets were first introduced on a state by state basis in the US, some US states are now starting to commit to targets for battery storage. So far, California and Oregon have set targets for the development of storage, with Massachusetts potentially the next to implement. California has stipulated that its three large investor-owned utilities (Edison International, PG&E, and Sempra) must commit 1,324 megawatts of storage by 2024, which is around 2% of California’s peak load.
Is energy efficiency real?
Energy efficiency is having an undeniable impact on electricity consumption. Energy intensity, a measure of energy consumption per unit of gross domestic product, declined by nearly one third between 1990 and 2015. Companies in the US are tending to report flat to negative load growth. Some US states, led by California, are promoting energy efficiency by decoupling utilities’ revenues from volume usage.
The driving force behind energy reduction is more energy-efficient homes and appliances. More homes are being insulated, efficient condensing boilers are replacing standard boilers, houses are being double glazed and appliances are more efficient. This trend in energy consumption per household will continue as buildings and appliances get smarter and more energy efficient.
Make hay whilst the sun shines
Rooftop solar has declined in cost significantly. The subsidies that many countries offer encourages residential customers to install rooftop panels on their homes.
Solar photovoltaic – lower costs, higher capacity
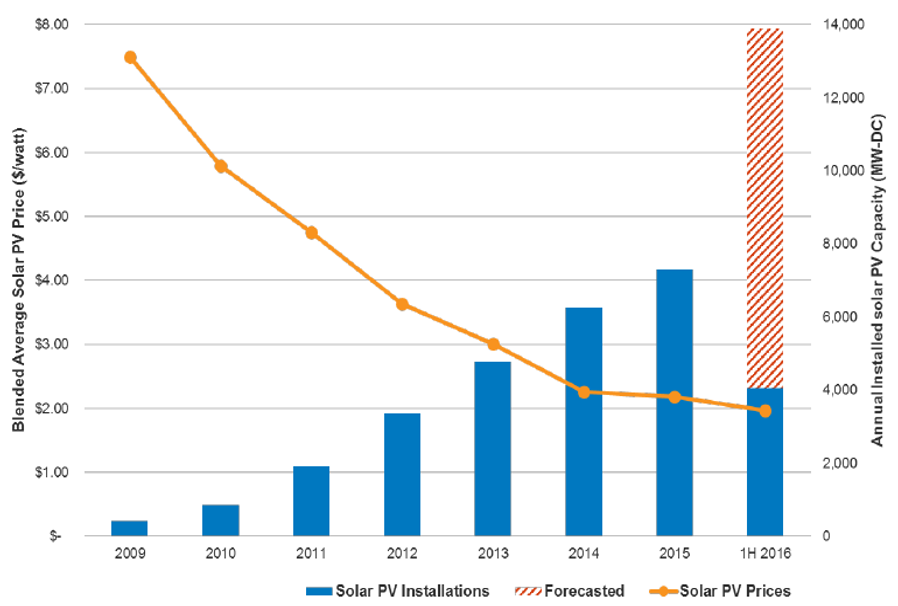
Source: Solar Energy Industries Association
However, a mismatch can occur between when solar energy is generated and when it is used. At these times, the distribution grid is used much like storage so that energy can be used when it is needed rather than when produced. For example, New York State is developing a system that compensates both the customer for excess energy sold to the grid, and the grid company for providing the transmission infrastructure to the household. New York aims to transform utilities such as National Grid and Iberdrola into distribution system platform providers, changing their responsibilities to include overseeing the interconnection of distributed resources. We believe this puts these utilities at the forefront of changes that could later be rolled out across other states with sunny climates.
Rebecca Sherlock is a Senior Investment Analyst at Colonial First State Global Asset Management. This article provides general information not specific to any investor's circumstances.