US Presidential elections can be divisive and unsettling. At times, the fate of the world seems to hang in the balance. But when it comes to investing, do elections really matter that much?
US voters will have their say in November 2024, but by maintaining a long-term focus, investors can position themselves for a brighter future regardless of the outcome at the voting booth. In fact, overreacting to short term volatility during election cycles can be detrimental to investment returns.
In this guide, we address questions about investing in an election year, drawing insights from our analysis of over 90 years of investment data across 23 election cycles.
Which political party has been better for investors?
Investing during an election year can be tough on the nerves, and 2024 promises to be no different. Indeed, politics can elicit strong emotions and biases, but investors would be wise to tune out the noise and focus on the long-term.
That’s because elections have, historically speaking, made essentially no difference when it comes to long-term investment returns.
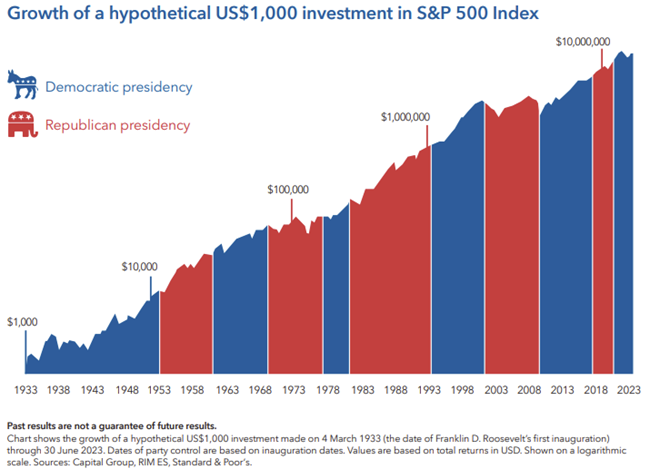
What should matter more to investors is staying invested. A US $1,000 investment in the S&P 500 made when Franklin D. Roosevelt took office would have been worth over US$19 million as at 30 June 2023. During this time there have been eight Democratic and seven Republican presidents.
Current economic and political challenges may seem unprecedented but a look at past election cycles shows that controversy and uncertainty have surrounded every campaign. And in each case the market has continued to be resilient over time. Successful investors stay the course and rely on time in the market rather than timing the market.
Bottom line: US stocks have trended up regardless of whether a Democrat or Republican won the White House.
What typically happens to the stock market during election years?
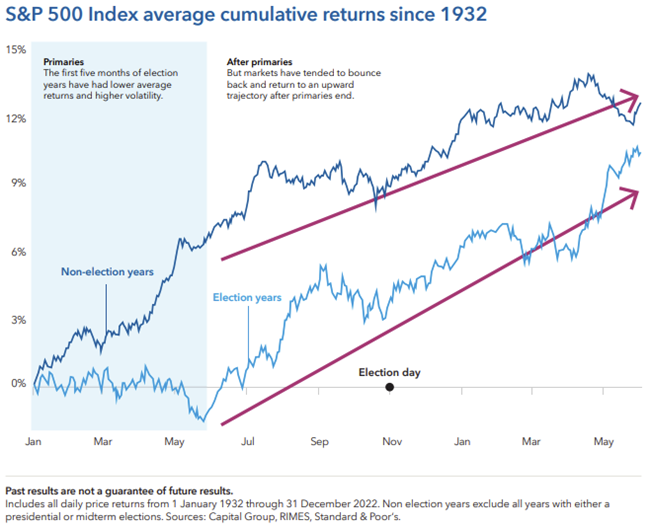
Markets hate uncertainty, and what’s more uncertain than primary season of an election year? With so many candidates on the campaign trail, the range of outcomes can feel daunting.
But the volatility is often short lived. After the primaries are over and each party has selected its candidate, markets have tended to return to their normal upward trajectory.
Patient investors who stay the course have often been rewarded. Since 1932, stocks have gained an average of 11.3% in the 12 months following the conclusion of the primaries (using 31 May as a proxy) compared to just 5.8% in similar periods of non-election years.
But keep in mind, these are just averages. Investors shouldn’t try to time an entry point into the market. Instead, a long-term approach can help investors withstand volatility and feel confident that markets have tended to move higher over time, even in election years.
Bottom line: Primary season tends to be volatile, but markets have bounced back strongly thereafter.
Which sectors have done best in election years?
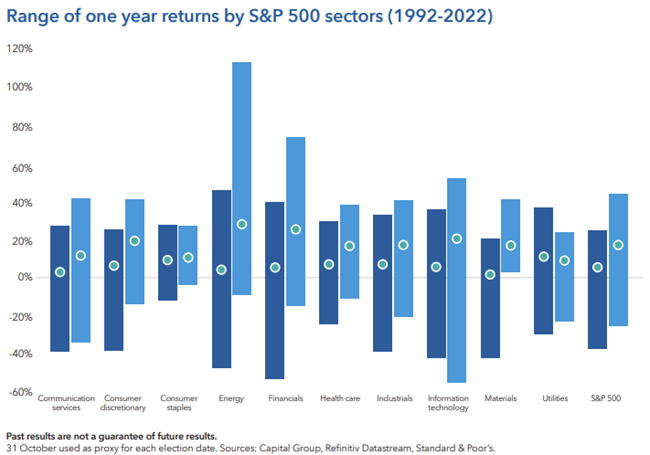
It‘d be great if there were go to sectors to invest in every election year, but unfortunately investing isn’t that simple. Every election cycle brings its own parade of candidates with their own policy agendas, so market winners and losers are hard to predict.
The health care sector has been in the crosshairs for a number of election cycles. Heated rhetoric over drug pricing put pressure on many stocks in the pharmaceutical and managed care industries. Other sectors have had similar bouts of weakness prior to elections.
Does that mean you should avoid a particular sector altogether? Not according to Rob Lovelace, an equity portfolio manager with 37 years of experience investing through many election cycles. “When everyone is worried that a new government policy is going to come along and destroy a sector, that concern is usually overblown,” Lovelace says.
Regardless of who wins, stocks with strong long-term fundamentals will often rally once the campaign spotlight fades. This pre-election market turbulence can create buying opportunities for investors with a contrarian point of view and the strength to tolerate short term volatility.
Bottom line: Election year volatility can create buying opportunities for long-term investors.
What have been the best ways to invest in election years?
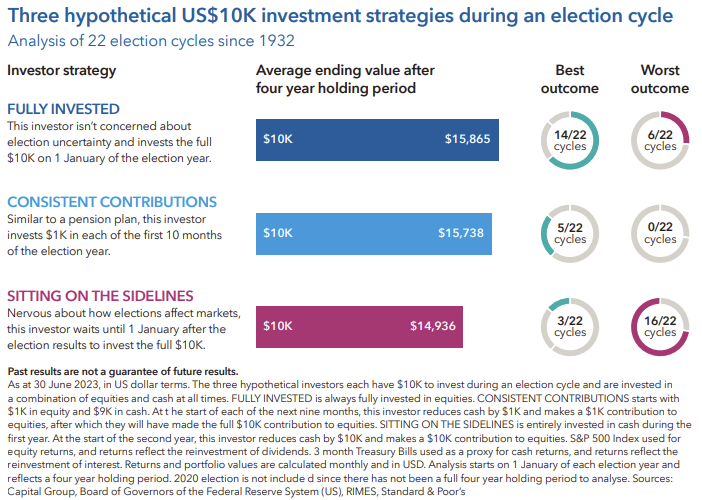
Spoiler alert: The best way to invest in an election year has rarely been by staying on the sidelines.
To verify this, we looked at three hypothetical investors, each with a different investment approach. We then calculated the ending value of each of their portfolios over the last 22 election cycles, assuming a four-year holding period.
The investor who stayed on the sidelines had the worst outcome 16 times and only had the best outcome three times. Meanwhile, investors that were fully invested or made monthly contributions to a pension plan, for example, during election years came out on top. These investors had higher average portfolio balances over the full period and more frequently outpaced the investor who stayed in cash longer.
Sticking with a sound long-term investment plan based on individual investment objectives is usually the best course of action. Whether that strategy is to be fully invested throughout the year or to invest on a regular basis, the bottom line is that investors should avoid market timing around politics. As is often the case with investing, the key is to put aside short-term noise and focus on long-term goals.
Bottom line: Staying on the sidelines has rarely paid off. It’s time, not timing, that matters most.
Capital Group Australia is a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article contains general information only and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. Please seek financial advice before acting on any investment as market circumstances can change. Download the full report here (personal details required).
For more articles and papers from Capital Group, click here.