Executive summary
1. The impact of the internet of things (IoT) is the ability to leverage real-time data to drive real-time decisions that can bring broad-based economic benefits to companies and consumers.
2. In the context of ‘smart factories’, IoT-enabled automation has led to a dynamic landscape for incumbent industrial automation vendors as they seek to offer integrated hardware-software solutions for industrial customers, i.e., manufacturers. To do so, vendors are either building or buying software capabilities, or partnering with software companies or doing all of the above. Their manufacturing know-how is a key advantage over potential new entrants.
3. Pure software companies are also entering the industrial automation space, and their business models are evolving. A change from traditional licensing models to subscription-based models can bring better customer insights to drive product offerings, but whether this will be acceptable to industrial customers is yet to be seen.
4. The demand from industrial customers for universal, open standards in industrial infrastructure — a change from today’s proprietary, closed architecture — is likely to change the profit equation for existing vendors. Open standards allow factory systems, supply chain, and customers to communicate seamlessly and realize the full benefits of IoT-enabled automation. The industry is likely to move in this direction despite resistance from existing vendors.
5. Investing in this space requires a global and cross-sector view of industrial automation to determine who will benefit from these trends. It is clear that new profit pools are being created as IoT is incorporated into factories (and elsewhere), offering a broader investment opportunity set for active research and management. Our global research platform generates critical insights that help us continually test the investment theses for our industrial automation holdings and spot emerging opportunities in software and other cutting edge technological areas such as machine vision and robotics.
Manufacturing is going through an extended IoT-enabled automation refresh cycle. This is likely to change the traditional global industrial automation vendor landscape as they have to offer new software capabilities in order to be successful in the changing marketplace. The MFS capital goods and technology sector teams did a global cross-sector analysis to assess the impact of IoT-enabled automation in manufacturing and its investment implications.
Impact of real-time information and analytics
The graphic below shows an example from rail operations. Using a continuous data feed from a physical system (a locomotive and its environment), a digital model can be built to simulate live operations, to the extent where the ‘digital twin’ can optimise the locomotive’s journey by controlling speed and braking. The result can be significant savings from the efficient operation and predictive maintenance of the physical system.
IoT-enabled rail operation and predictive maintenance
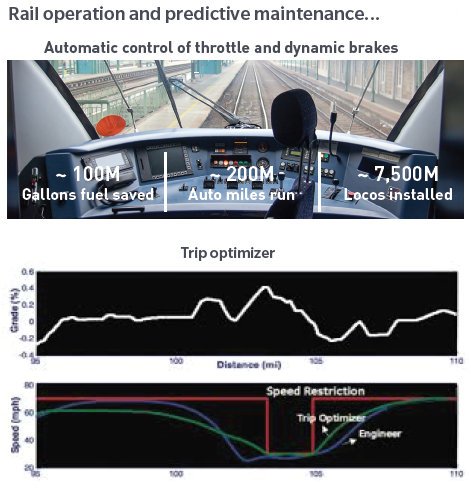
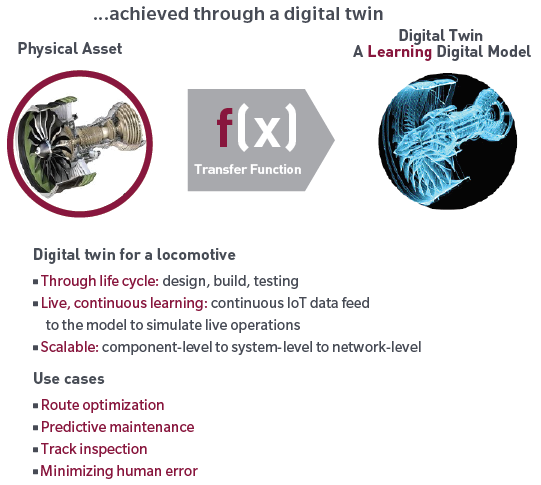
Source: Adapted from GE, “Digital Twin for the Railway Network,” 2018.
Implication for industrial automation and software companies
In the context of ‘smart factories’, IoT-enabled automation has led to a dynamic landscape for incumbent industrial automation vendors as they seek to offer integrated hardware-software solutions for industrial customers, i.e., manufacturers. To do so, vendors are either building or buying software capabilities, or partnering with software companies or doing all of the above. Their manufacturing know-how is a key advantage over potential new entrants. Pure software companies are also entering the industrial automation space, and their business models are evolving.
A change from traditional licensing models to subscription-based models can bring better customer insights to drive product offerings, but whether this will be acceptable to industrial customers is yet to be seen. The demand from industrial customers for universal, open standards in industrial infrastructure — a change from today’s proprietary, closed architecture — is likely to change the profit equation for existing vendors.
Open standards allow factory systems, supply chain, and customers to communicate seamlessly and realize the full benefits of IoT-enabled automation. The industry is likely to move in this direction despite resistance from existing vendors.
Conclusion
The traditional industrial automation landscape is changing from an IoT-enabled automation refresh cycle, and the winners and losers are still in the making. Investing in this space requires a global and cross-sector view of industrial automation to determine who will benefit from these trends. It is clear that new profit pools are being created as IoT is incorporated into factories (and elsewhere), offering a broader investment opportunity set for active research and management. Our global research platform generates critical insights that help us continually test the investment theses for our industrial automation holdings and spot emerging opportunities in software and other cutting-edge technological areas such as machine vision and robotics.
To learn more, please read our white paper on the subject.
Thomas P. Crowley, CFA, Bradford J. Mak, and CV Rao, CFA are Equity Research Analysts at MFS Investment Management. The comments, opinions and analysis are for general information purposes only and are not investment advice or a complete analysis of every material fact regarding any investment. Comments, opinions and analysis are rendered as of the date given and may change without notice due to market conditions and other factors. This article is issued in Australia by MFS International Australia Pty Ltd (ABN 68 607 579 537, AFSL 485343), a sponsor of Cuffelinks.