I recently returned from a two-week, coast-to-coast trip across the United States, talking to institutional clients, pension funds and investment consultants. The mood on the ground is one of caution. Rising inflation and interest rates are on everybody’s mind. A war in Europe and spiking oil prices are creating uncertainty. And the possibility of recession hovers at the edge of conversations. During such a period, it’s easy to wonder if there are any safe ports in the investment storm.
In this environment, we believe that infrastructure has an important role to play in portfolios. Investments in assets such as toll roads, airports, railroads, utilities and renewables, energy midstream, wireless towers and data centres show their worth in such times. These types of investments have high barriers to entry, structural growth and strong pricing power, giving them the potential to withstand inflation and generate consistent earnings, regardless of the broader economic backdrop.
With this in mind, below are three reasons we believe infrastructure investors may be well-placed to weather the geopolitical storms ahead.
1. Infrastructure runs its own race - Recent performance has seen the asset class hold up relatively well as global equities sold off, consistent with its history of providing most of the upside in rising equity markets but offering protection from falling ones. This pattern of performance is underpinned by global listed infrastructure’s consistently strong pricing power, predictable cash flows, and relative immunity to economic cycles.
This ability to hold up in falling markets has enabled the asset class to generate higher returns than global equities over the past 20 years, with less risk, as measured by standard deviation of returns.
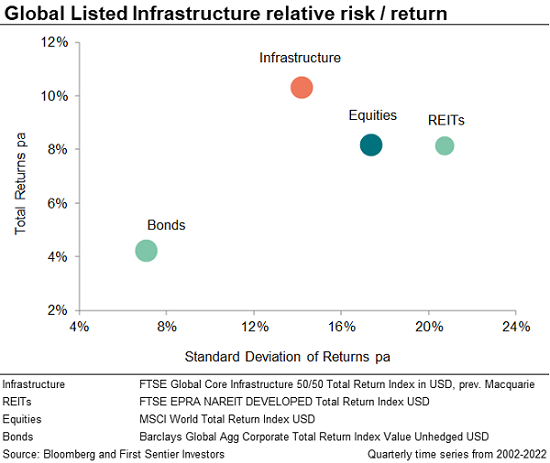
2. Infrastructure is a price maker, not a price taker - Global listed infrastructure has historically outperformed global equities against a backdrop of high inflation[1]. This is a reflection of the fact that infrastructure’s tangible assets provide essential services, using contracted or regulated business models.
These assets consistently demonstrate the ability to pass though the effects of higher input costs and inflation, to the end user. This can be achieved in several ways – for example by allowing utilities to earn regulated real returns; or via contracts which explicitly link tolls and tariffs to the inflation rate; or as a result of regional oligopolies’ robust industry structures allowing inflation pass-through.
Australian-listed Transurban, for example, is a beneficiary of improving traffic volumes that have rebounded following the lockdowns of the last two years, while the concession terms on the vast majority of its road networks allow tolls to be raised by the rate of inflation.
Infrastructure’s capital-intensive nature provides high barriers to entry which have allowed incumbent operators in other sectors, such as mobile towers and freight rail, to achieve similarly robust pricing results even without explicit inflation links. Our analysis has found that more than 70% of assets owned by listed infrastructure companies have effective means to pass through the impacts of inflation to customers, to the benefit of shareholders. This number is closer to 80% for our portfolio today.
Further, the value of infrastructure assets can generally be expected to rise during inflationary environments. Existing infrastructure assets become more attractive as the replacement costs increase. This factor gives infrastructure assets enhanced appeal during periods of high inflation.
3. Infrastructure taps into the big themes – Many of the mega-trends shaping today’s world have infrastructure at their heart. Decarbonisation is a good example – as the world looks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, we need more renewable energy generation, distribution and storage facilities. Similarly, the growth of electric vehicles demands widespread electrification and public charging infrastructure, which investors can support by allocating capital to its development.
Midwest US electric utility Xcel Energy has been one of the most active electric utilities in the US transport electrification space. It plans to invest around US$2 billion to support 1.5 million electric vehicles by 2030, through infrastructure such as charging stations and grid upgrades.
The move to renewable energy is reshaping the dynamics of the utilities sector, which has traditionally been seen as a defensive but typically lower-growth segment of the market. However, these types of assets, which account for around half of the listed infrastructure opportunity set, are now seeing a shift driven by the investment opportunities presented by the build-out of renewable energy. Some utility companies are ramping up annual earnings growth forecasts from a 4-6% range to 5-7% or even 6-8%.
For example, Texas-based CenterPoint Energy is focused on achieving its net-zero goals by 2035 by building out its renewable resources and retiring coal plants. The company now expects to grow earnings per share by between 6% and 8% each year between 2022 and 2030, as it earns a return on the extensive work that it will carry out in this area.
Digitalisation is another key theme. Ever-increasing demand for wireless data / connectivity continues to underpin steady earnings growth for Towers and Data Centres, insulating them from the ebbs and flows of the broader global economy. The changes required during the pandemic have already led to a greater reliance on wireless data in many people’s everyday lives. The adoption of 5G technology over the medium term will require networks to handle increased data speed, and a much higher number of connected devices.
While global markets remain unpredictable, we are confident in global listed infrastructure’s ability to benefit from these structural themes over the long term.
[1] Source: First Sentier Investors and Bloomberg, as at 26 May 2022.
Trent Koch is Portfolio Manager, Global Listed Infrastructure at First Sentier Investors (Australia) Ltd, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This material contains general information only. It is not intended to provide you with financial product advice and does not take into account your objectives, financial situation or needs.
For more articles and papers from First Sentier Investors, please click here.