Fearmongering about Australia’s ageing population has ramped up again recently. The headline in the image below is a classic example.
Source: Australian Financial Review
Three years ago, I wrote a report about the myths surrounding the population and ageing debate. Find that report here. It debunks much of the nonsense analysis we see repeated uncritically in the mainstream press. I discuss some of the main points below.
Ageing does not imply fewer workers
Currently, Australia’s population is the oldest it has ever been on average. The population share aged over 65 has increased from about 12% to 16% since 2000. Despite this, the proportion of the population working is the highest ever. Over 64% of all Australians, including children and the elderly, are currently working. That’s up from 59% two decades back in 2000.
The one-third increase in the share of over-65s is roughly the same proportional increase we can expect over the next half-century. Yet for some reason, we are meant to panic about it.
Another weird aspect of the ageing debate is how one argument is silently transformed into another. The main argument is that ageing means fewer people aged 15-64s compared with those over 65. But this is somehow transformed into fewer workers supporting non-workers (and sometimes further transformed into stories about your personal tax bill). But this does not need to follow, as the above data shows.
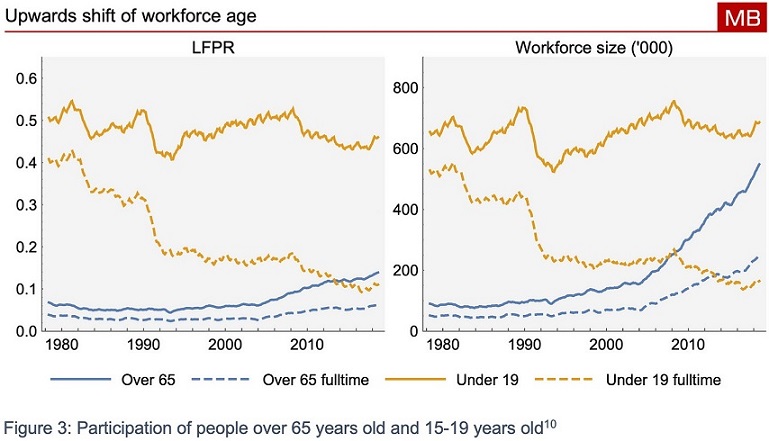
In fact, there is an increasing share of over-65s who are working and a declining share of under-19s. There are now more over-65s working full-time than under-19s working full-time. So why don’t we adjust our age structure metrics to reflect actual modern working lives? I would argue if we did that it would be obvious that there is nothing to fear about ageing (below, LFPR means Labour Force Participation Rate).
Ageing isn't related to economic growth
A 2017 study by economists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) found
“...that even when we control for initial GDP per capita, initial demographic composition and differential trends by region, there is no evidence of a negative relationship between aging and GDP per capita; on the contrary, the relationship is significantly positive in many specifications.”
The charts below show a similar relationship.
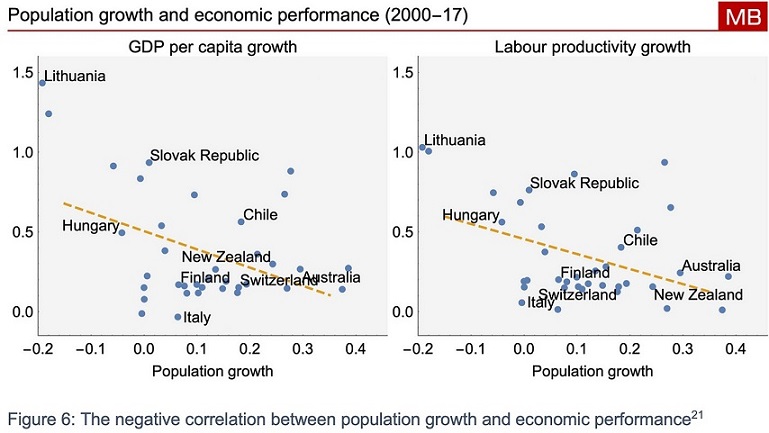
The relentless uncritical talk of the perils of ageing in Australia’s mainstream media has given a distorted view of the world. There is more detail about the growth and ageing issue in my report.
High immigration doesn’t change the age structure much anyway
This is the most bizarre part of the whole story. We know every immigrant ages at the same rate as everyone else. Even if you believe that ageing is a problem because the proportion of workers in the economy might decline (despite the facts) the solution is to get more people working.
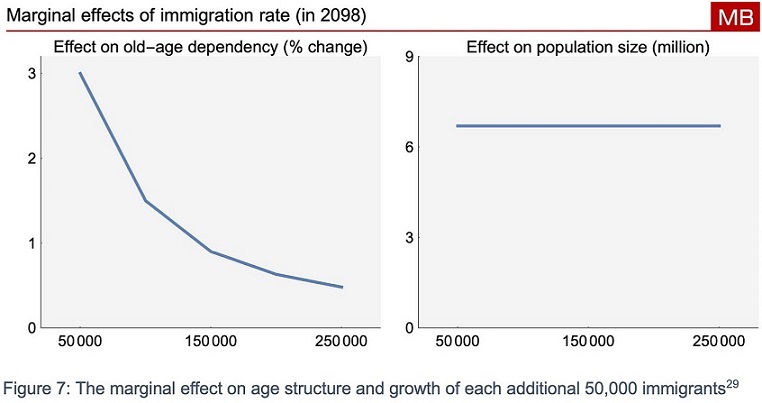
The effect of immigration on the age structure is not linear. In fact, it is easy to show that a large effect on the age structure can be achieved by relatively few migrants. Age structure simulations have shown that
“the largest and demographically most efficient impact of immigration on ageing occurs with the first 50,000 net migrants and that the impact reduces significantly with each additional 50,000 net migrants.”
I show this in the charts below. By the end of the century, an immigration rate of 50,000 per year reduces that share of the population aged over 65 by 3%. The next 50,000 per year only further decreases this population metric by 1.5%. The next 50,000 after that decreases the metric by less than 1%.
In short, to get twice as large an effect as the first 50,000 per year immigration on the ratio of over 65s as a share of the population (if indeed you care about that metric), you would need to not just double the rate of immigration but quadruple it to 200,000 per year.
So what?
If you want a big Australia, then make your argument for it. But don’t pretend that the age structure of the population is the reason why.
Dr Cameron Murray is an Economist and co-author of the Book Game of Mates. Subscribe to his written work at Fresheconomicthinking.substack.com. This article is general information.