US equities rule global markets, but history is littered with examples of markets that seemed invincible — until they weren’t.
Forecasting market returns is a fool’s errand, as history has repeatedly shown. Few predicted the 2023 AI-fuelled US tech rally after a bruising 2022, or the sharp bond selloff caused by stubborn inflation. There’s only one certainty: markets remain unpredictable. It’s a feature, not a bug.
For the past decade, US equities have been the undisputed stars, delivering an extraordinary run. The S&P 500, powered by the FAANG/Magnificent Seven stocks1, has vastly outperformed the majority of its global peers, giving rise to the US exceptionalism narrative.
But no market dominates forever. Japan ruled the 1980s, emerging markets were the darlings of the 2000s, and even Europe has had its moments in the sun. The US, while formidable, is not immune to weak performance.
This raises a critical question for investors: should you go 'all in' on US equities, riding the momentum of their recent strength, or should you consider a more diversified approach? After all, the smart money forecasts risks, not returns.
Diversification isn’t always as it seems
The conventional response is to allocate to global equities, such as the MSCI All Country World Index (ACWI), which spreads exposure across regions but remains heavily skewed towards US equities. That means a downturn in the US — whether sparked by rising interest rates, US President Donald Trump’s policies, Chinese AI developments, or any other unknown — can still leave your portfolio vulnerable.
Shifting the focus from returns to risk and constructing a portfolio that allocates based on diversification and risk balancing can produce a more robust solution. As Figure 1 shows, the ACWI concentrates heavily in US equities, while a risk-based approach allocates more evenly across regions such as Europe, Japan, and emerging markets. This ensures portfolios are better diversified and less tethered to the fortunes of one economy.
Figure 1. A balanced approach to global diversification
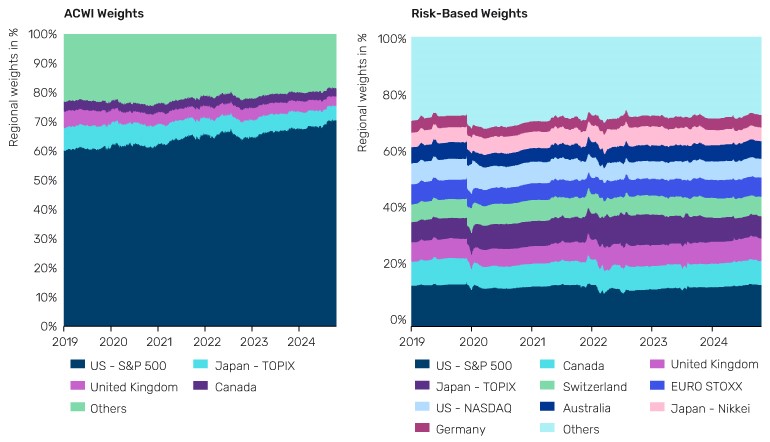
Source: MSCI, Man Group, as at January 2025.
While the S&P 500 has delivered strong returns over the past two decades, a risk-based allocation has delivered better risk-adjusted returns. As Figure 2 shows, a risk-based allocation outperforms both the S&P 500 and the MSCI ACWI Index in terms of Sharpe ratio (i.e., investors are better compensated for every unit of risk they take on). Crucially, this approach doesn’t require a crystal ball. It is not about predicting the next big winner but about creating a portfolio that is designed to navigate diverse market conditions without sacrificing upside potential.
Figure 2. Better risk-adjusted returns
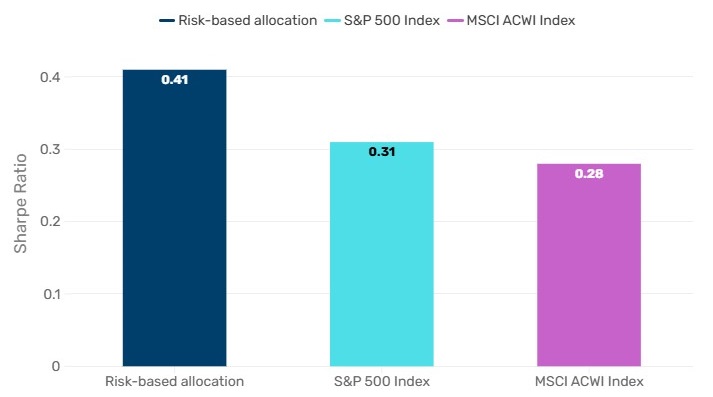
Source: Bloomberg, Man Group, as at January 2025.
In equity investing, while risk-adjusted metrics like the Sharpe ratio are valuable, they rarely satisfy investors on their own. In risk-on environments, the focus inevitably shifts to delivering absolute returns — because, as the old adage goes, ‘you can’t eat Sharpe ratio.’
As Figure 3 highlights, a risk-based allocation strategy not only outpaced the MSCI ACWI but also kept pace with the S&P 500, doing so at a lower volatility — a compelling proposition for investors.
Figure 3. A smoother ride – the returns of a risk-based approach compared with the MSCI ACWI and the S&P 500
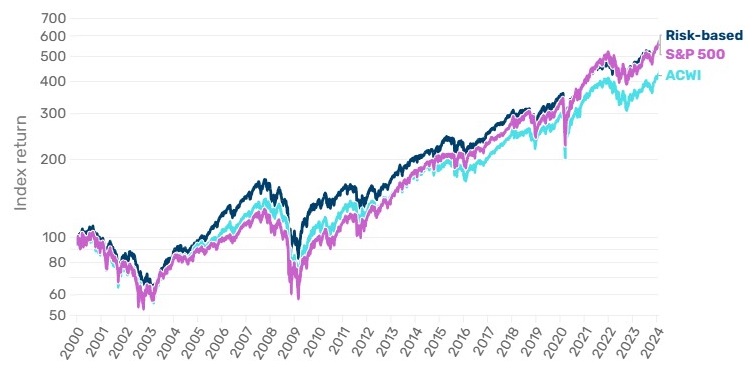
Source: Bloomberg, Man Group, as at January 2025.
The allure of US equities is understandable. They have been the stars of the investment world for years, and their track record is hard to ignore. But history is littered with examples of markets that seemed invincible—until they weren’t.
So, before you go 'all in' on the US juggernaut, consider whether there’s a better way to diversify. Because in investing, as in life, betting everything on one idea is rarely the safest path.
All data Bloomberg unless otherwise stated.
1. FAANG was the original group of tech superstar stocks Facebook (now Meta Platforms, Inc.), Amazon, Apple, Netflix, Google (now Alphabet, Inc.), that morphed into the Magnificent Seven, dropping Netflix, and adding Nvidia, Tesla and Microsoft.
Contributors: Tarek Abou Zeid, Partner, Client Portfolio Manager, Man AHL, Peter Weidner, Head of Total Return Strategies, Man AHL, Max Buchanan, Client Portfolio Management Analyst, Man AHL and Katerina Koutsouri, a quantitative analyst at Man AHL. Man Group is a fund manager partner of GSFM, a Firstlinks sponsor. The information included in this article is provided for informational purposes only.
For more articles and papers from GSFM and partners, click here.