Faced with recent governance problems, market regulators and financial advice businesses have focused on minimising the likelihood of past product and advice failures being repeated. There are also other distractions such as licencing restrictions, skill shortages, asset class bubbles etc. These events will lead to evolutionary changes, much as occurred following previous reforms (such as SIS Act 1993, MI Act 1998, FSR Act 2001), product and service innovations (such as mastertrusts, wraps, SMSFs etc.) and competitor entries and exits. But most importantly, the industry is confronting significant challenges that will cause revolutionary changes and will impact the way financial services advice is delivered and paid for.
Digital tsunami
These revolutionary changes are occurring in the areas of digital transformation and technology take-up and are likely to be game-changing to many industries, including financial advice services.
Melodramatic? We don’t think so. Look at the impact digital technologies has had and are having on some other industries: Amazon and ereaders replacing firms like Borders, RIM and Nokia suffering due to changing digital landscapes, Skype impacting fixed line telcos, LinkedIn and Seek affecting traditional recruiting firms, Uber and Airbnb challenging taxi and hotel industries respectively.
In financial services, over 75% of US trades are performed by ‘algo-trading’ engines. Into the future it is foreseeable that cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin will pose a threat to payments processors (banks), tax collectors (governments) and foreign currency traders.
Superficially it is easy to argue that our industry is vastly different to music, travel, books etc, but much of the financial services offered are intangible, standardisable and consequently, digitisable.
Let’s dive a bit deeper. At a macro level, our industry is confronting a veritable ‘digital tsunami’ which will have multiple fronts hitting concurrently. We will consider the following six fronts:
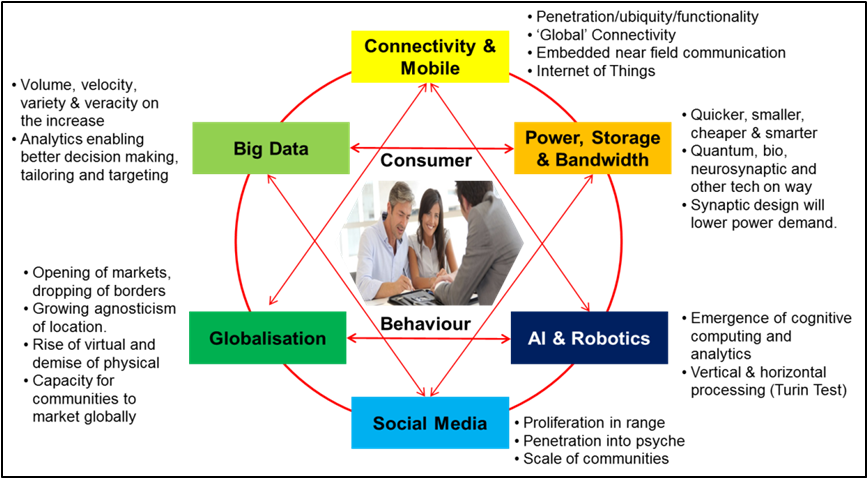
1. Big data: Volume and velocity of data is rapidly increasing with the growth of the internet, mobile connectivity and ‘Internet of Things’ (IoT) devices (see also What is the Internet of Things?). In the process of creating data, we leave digital footprints which can be monitored, analysed and used for predictions about our purchasing behaviour. Even though privacy of such ‘footprints’ are an issue, firms can now develop new products and services and provide enhanced customer experience by harnessing capabilities such as data analysis, predictive modeling, social network mapping and listening.
2. Power, storage and bandwidth: Smaller, faster, cheaper and smarter could describe the inexorable growth in these three infrastructure enablers of the tech revolution.
This ‘power of exponential development’ means, what has been achieved to date will pale into insignificance with that on the horizon. The biggest leaps are coming!
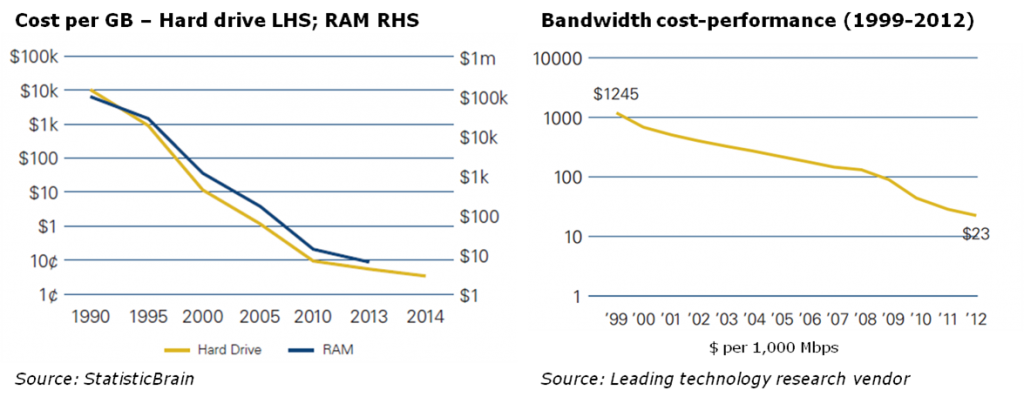
As demonstrated in the diagrams below, dramatic improvements in cost-performance are contributing to exponential growth in digital technologies. These have also been the key drivers of innovations in mobile and cognitive computing, IoT devices and AI.
Number and size of transistors bought per $ (Source: Extremetech)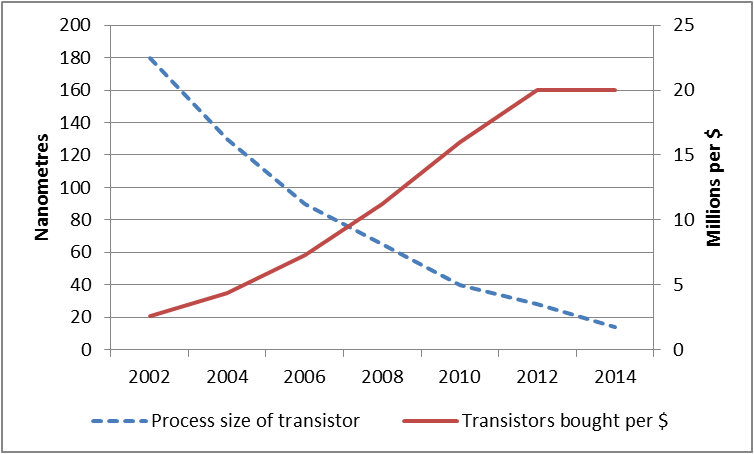
3. Social media: The emergence of social media and the volume of user-generated content that it has produced is one of the greatest sociological phenomenon in human history.
In financial services, smaller firms should be cognisant of several aspects to social media. A LinkedIn-Cogent study found a disconnect between an investor’s preparedness to engage through social media and what advisors do, i.e. potential ‘service mis-alignment’. Other opportunities in this space are ‘social listening’ and ‘customer collaboration’.
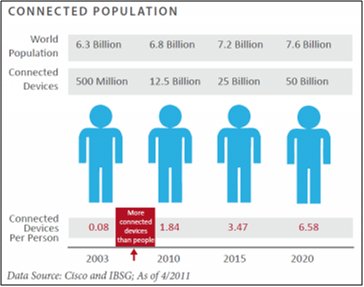
4. Connectivity and mobile: Connectivity has become ubiquitous for most of the world’s population and connected devices are dematerialising many other devices and businesses by converging the capabilities into the one device. (For a thought-provoking read see Harvard Business Review’s ‘How Smart, Connected Products Are Transforming Competition.’) For instance, 28% of Australians in 2013 owned at least three connected devices which is up from 10% two years earlier. Gartner believes that 26 billion units will be deployed and incorporated by 2020.
Financial services is an information-based business. Consequently IoT presents incredible opportunities to tailor products and services, provide special offers etc.
5. Artifical Intelligence (AI): We are inching ever-closer to the time where machines will exhibit intelligent behaviour indistinguishable from that of a human and interact in natural languages using ‘cognitive analytics and computing’.
For example, IBM’s Watson has been opened up to the financial space and is now capable of performing deep content analysis and evidence-based reasoning to accelerate and improve decisions, reduce operational costs, and optimise outcomes.
6. Globalisation: Technology can be seen as one of the most potent enablers and drivers of globalisation which opens up a world of competent and available resources.
Traditionally, large players have taken advantage of the globalisation conveyor but smaller players now could consider outsourcing administrative functions such as meeting note transcriptions, data entry, paraplanning, SMSF administration etc.
We should also be concerned about potential entries from global players because access to our market may be more cost effectively attained via technology (platform engines and robo advice tools etc). For instance, leveraging off US-based investment platforms or account aggregation systems.
The point of convergence
If all these six fronts do converge then the financial services advice space is about to be disrupted. The ensuing change is set to unleash on traditional consumer behaviour and their decision-making frameworks, on what services people want, when they want them and at what price. Hence, how we react will determine how we prosper.
As demonstrated below, investors can be grouped into three major camps depending on their financial services needs, lack of time and inclination etc. An increasing number of investors are being categorised as ‘self-directed’ and we believe strategic planning should consider the following 2x2 schematic and the listed suggestions:
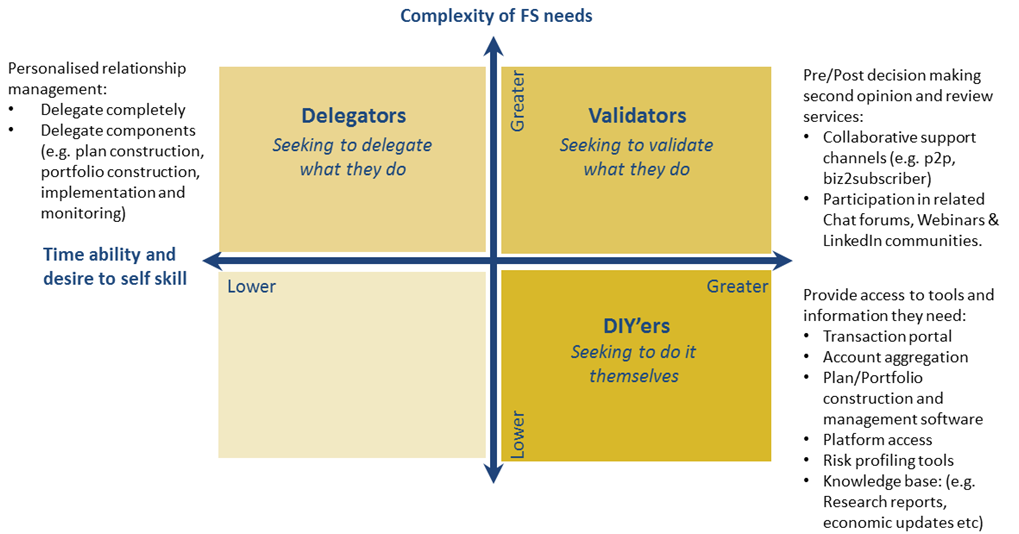
Source: PHAROS Financial Group
In summary, consumer behavioural change is set to rock to its core our traditional ‘delegated’ advice model and the way we do business. The two key takeaways from this article are: ‘Power of exponential growth’ means great technological leaps are ahead not behind and investor behaviours are changing towards ‘self-directed’ driven by innovations in financial services. Although, some may not be concerned with these developments due to their existing client base and belief in that ‘people buy from people’, the rest – especially those building a business for the future – should start to enquire and research.
Giulio Russo is General Manager at Madison Financial Group Pty Ltd. This article is a summary of the PHAROS/Madison Financial Group White Paper No. 1 on digital disruption.