Now that all companies in Australia have reported, it’s the ideal time to step back and draw some conclusions. Like every year, there were winners and losers aplenty. In the flurry of announcements, it’s easy to get caught up in jumping from one result to another and not take the time to work out what is important. For us the key themes that stood out from reporting season were: inflation, consumer spending and cashflow.
How companies manage inflation is the big differentiator
High inflation is a problem that companies haven’t had to deal with for years, and many newer companies have never had to deal with. Take a look at this graph of Australian CPI inflation over the past 20 years.
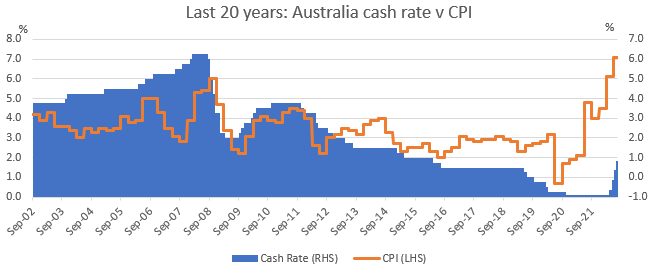
Source: Factset, 15 August, 22
Prior to this year, inflation hasn’t been above 5% since 2008 or above 3% since 2011. Over the past 10 years, companies that didn’t have strategies in place to manage high inflation weren’t punished for it. Not any longer. While the competitiveness of an industry or sector has a significant impact on how easy it is for companies to pass on inflationary costs, there were also many reporting season examples of companies that suffered from being less organised or disciplined in their inflation management.
For example, companies might have left pricing decisions in the hands of sales teams without setting proper controls, or not had any centralised oversight of how their supply chain costs were increasing. The building materials sector was a key offender here.
On the other hand, companies that were proactive and had strategies in place to deal with inflation - like dynamic pricing, CPI built into contracts, or a strong market position that gave them the ability to pass on cost increases (like Brambles, Amcor, and Aurizon) - reported better results in general.
Outlook for inflation
The feedback from our one-on-one meetings with companies is that inflation will continue to be high. Why? Nearly all companies have old contracts that are yet to be rolled to current market pricing across key cost lines. For example:
- The largest is employment contracts. Award wages in Australia have just risen in July by 5.1%, and 6.5% in New Zealand, and these increases will result in similar increases to enterprise bargaining agreements (EBAs) across the country when agreements come up for renewal. When these EBAs are renegotiated, this will ‘lock-in’ wage increases of 4-5% p.a. for the next three years.
- Electricity contracts typically last 1-3 years and when these roll over they will increase significantly, in many cases up 100%+.
While inflation seems to be coming off its peak, it looks like high inflation will be with us for some time. During reporting season, we saw big differences in margin outcomes due to how proactive businesses were in managing inflation and we think this will continue to be an important factor driving financial performance.
Consumer spending stayed strong, but for how long?
Reporting season showed that the large end of corporate Australia is in pretty good health. And, so far, we’re not seeing consumers pulling back on their elevated spending habits post Covid. Retail sales rose 1.3% in July. We saw strong sales results from Myer, Breville and Super Retail Group. We’re only seeing isolated examples of reduced spend, particular in online ‘at home’ categories, which we witnessed in Kogan’s results.
Why? Two main reasons:
- Many people saved money during peak COVID with less travel and entertainment and low interest rates and so they can maintain spending for a certain amount of time.
- Rising interest rates aren't affecting people’s spending much, yet. There is around a three-month lag between when banks raise their rates and when they start impacting mortgage-holders’ household budgets. This is due to the way banks pass on interest rates with mandatory notification periods and the way they change the capital versus interest rate portion of repayments. Given interest rates were first lifted in May, higher rates have only just started to hurt.
We say ‘so far’ because undoubtedly consumer spending can’t stay above trend forever. A global slowdown is coming, the question is to what degree. Europe looks like it will head into recession and the US and Australia may well follow. Even if Australia avoids recession, spending here will slow due to continued inflation of essentials and rising interest rates.
Cashflow suffered and will remain an issue for many
Many companies have had cashflow issues over the past six months and the main reason for this is their rising inventory balances (cost and volume), leaving them less cash to spend. This is partly due to the rising cost of goods, but also due to many companies deliberately increasing their overall inventory levels.
Businesses are holding larger-than-normal inventories because they have been worried about supply chain issues and inflation. They’ve been worried that they can’t access things they need to keep their businesses running AND they’re worried about the rising cost of everything. So they have been ordering more than normal to lock in lower costs and to make sure their businesses keep chugging along (as demonstrated in the results from Reece and Reliance Worldwide).
As well as excess inventory, if companies made poor inventory decisions, then it had big consequences on their profit margins. Companies that ordered too much either have to hang onto it, dump excess inventory, or reduce prices to get rid of it – Walmart and Target are well-known US examples of this. Supply chain issues seem to be easing in many areas, which will help alleviate this issue, but many companies still need to work through their higher inventory levels without impacting profits.
The three big ones
Inflation, consumer spending and cashflow were the big three issues that we saw impacting earnings reports last month. The companies that have been dealing best with these issues are well-established with strong market positions and capable management teams that are navigating their way through these volatile times. While sharemarket falls can be tricky, it’s also a time of opportunity for investors. We’re still seeing high-quality companies at reasonable valuations.
Michael O’Neill and Daniel Moore are Portfolio Managers at Australian equities fund manager Investors Mutual Limited. For more in-depth discussion on key takeaways from reporting season, tune into an upcoming webinar.
This information is general in nature and has been prepared without taking account of your objectives, financial situation or needs. The fact that shares in a particular company may have been mentioned should not be interpreted as a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold that stock. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.