The Weekend Edition includes a market update plus Morningstar adds links to two additional articles.
Most investors love to buy stocks that others own, when what they should be doing is looking at ones that others ignore.
For instance, many large fund managers can’t buy small or microcap stocks because they’re too illiquid. They’ll often stay away from stocks that have fallen dramatically in value because they’ll get too many hard questions from asset consultants. And they’ll shun stocks with serious ESG issues, such as oil and coal, because they either have ESG mandates or risk losing investors in their funds.
Investors can take advantage of these constraints on institutions to get an edge in markets. Here’s a look at three strategies that can deliver market-beating returns.
Dogs of the Dow/ASX
In his 1991 book ‘Beating the Dow’, Michael O’Higgins outlined a strategy of investing in underperforming companies which he dubbed ‘Dogs of the Dow’. The strategy involves buying the ten worst-performing stocks from the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) from the past 12 months at the beginning of the year, and then selling them at the end of December. O’Higgins added one caveat: the stocks selected should be restricted to only those paying dividends.
The rationale behind the strategy is that the ten worst performing stocks in a given year will have gone down so far in price that investors hate them. Anyone who could have sold them probably has, which can mean there are few sellers left. Fund managers won’t want to hold onto these stocks at the start of a new year because they won’t want to justify owning them to asset consultants and their investors. In effect, these managers can become forced sellers of the stocks. And because the stocks are so deeply out favour, they're often trading at cheap prices.
The reason for restricting the strategy to the DJIA is that large caps are more likely to have the financial strength to stay in business. Adding a further filter of investing only in dividend paying companies helps to ensure that the stocks have the financial health to pay out a dividend from their profits.
How has the strategy performed? Hugh Dive from Atlas Funds Management has tracked a 'Dogs of the ASX' strategy over the past decade. In 2023, the average equal-weighted return of Dogs from the previous year returned 26% versus the ASX 200’s gain of 12%.
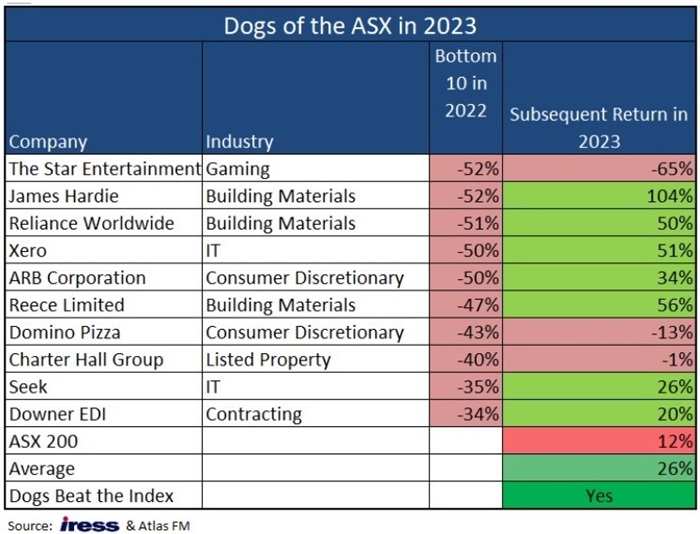
The best performers included James Hardie and Reece, which were sold down in 2022 on concerns of a US recession, only to come storming back last year as the recession never eventuated. Other gainers were IT companies which were hammered in the broader tech selloff of 2022, before bouncing hard in 2023.
Since 2013, the Dogs of the ASX have beaten the ASX 200 in 7 out of 10 years. Overall, the cumulative outperformance of the Dogs has been impressive.
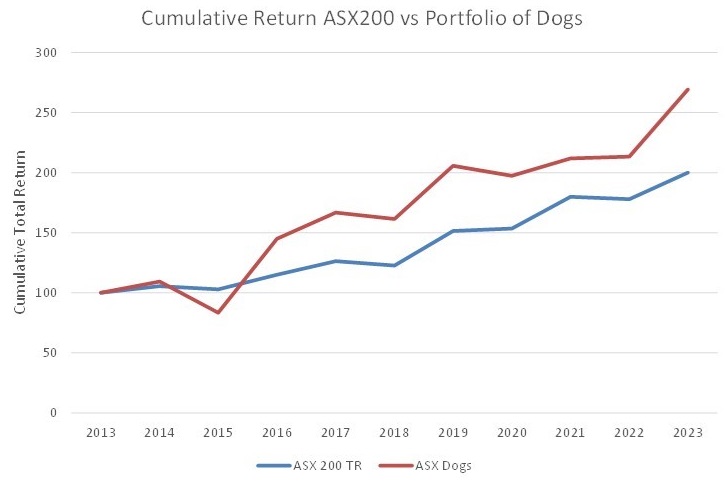
Source: Hugh Dive, Atlas Funds Management
Hugh Dive admits there are few fund managers who would be able to run this type of strategy. They wouldn’t be able to justify holding stocks with such bleak outlooks to asset consultants at the beginning of a year.
I would add another reason: it’s psychologically hard, even for a fund manager, to hold onto stocks that have tanked. It can be easier to put them in the too-hard basket and move on.
For the enterprising individual investor, though, that can provide potential opportunities.
Tobacco stocks
Morningstar’s Shani Jayamanne wrote a recent article on one of the best performing stocks of the past 100 years: Philip Morris. US$1,000 invested in the company in 1925 would be worth close to US$1 billion now. That’s an annual return of more than 15% over that period.
Philip Morris is a US-based tobacco company. It’s well known that tobacco has been a declining industry for decades. Smoking peaked in the US in 1961 and as its health issues became widely known, massive lawsuits against companies followed. Warning labels were slapped on products, governments restricted advertising of tobacco, and repeatedly raised taxes on companies.
The question is: how has Philip Morris performed so well on the stock market given these headwinds? One of the reasons is that investors have largely stayed away from the stock, particularly institutional investors. They haven't wanted to be part of the lawsuits, health warnings and bad press that have accompanied Philip Morris along the way. Not to mention the rise of ESG in the past 20 years and the restrictions that's placed on funds investing in ‘sin’ stocks.
Consequently, Philip Morris has traded at cheap levels for much of the period. A low share price does a couple things:
- It raises the cost of capital for a company. The means that Philip Morris and other tobacco companies have had higher return hurdle rates when it comes to new projects. Put simply, it's restricted them from undertaking aggressive expansion. It's also reduced competition from new companies. That's limited industry supply and consolidated the power of existing players such as Philip Morris.
- It allows a company to buy back shares at cheap prices. Philip Morris has regularly bought back shares over the decades, and that' paid off for investors.
Another contributor to the performance of Philip Morris and other tobacco stocks has been their ability to raise prices to cover increased taxes on their products. With declining tobacco volumes, increasing prices has been critical to boosting earnings for these companies over time.
US sector returns, 1900-2019
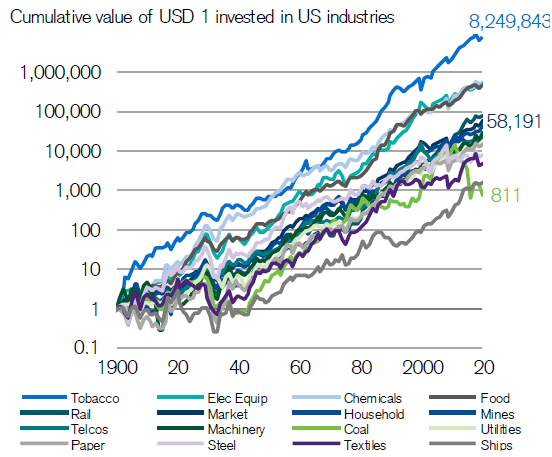
Source: Credit Suisse
Small/value stocks
Many institutions are restricted from buying small and microcap stocks for liquidity reasons. Small cap stocks don’t have enough turnover for these funds to establish meaningful positions.
It means there’s less investor demand for these stocks. Not only that, but there are likely to be few broker analysts covering the stocks. And limited media coverage of the stocks too. All of this increases the chances that these types of companies will be neglected and cheap.
A well-known fund manager, Dimensional Fund Advisors (DFA), was founded in 1981 to take advantage of these gaps in the market. The founders were largely influenced by the work of academics Eugene Fama (aka ‘The Father of Modern Finance’ or ‘The Father of the Efficient Market Hypothesis’) and his colleague Kenneth French, who developed a statistical model of asset prices, and observed that two classes of stocks tended to do better than the broader market: small caps, and stocks with high book-to-price ratios.
DFA took these observations and formed low-cost funds based on them. The success of the strategies has resulted in funds under management ballooning close to US$1 trillion.
DFA certainly aren’t the only firm to take advantage of small cap and value strategies to beat markets, though they're one of the largest and most well-known.
***
In my article this week, I look at the rout in battery metal prices and the lessons for investors.
James Gruber
Also in this week's edition...
The major Australian banks have had a nice run of late as markets start to factor in a soft landing for the economy. But Firetrail's Scott Olsson believes that the market is overlooking some earnings headwinds that are likely to put pressure on bank share prices this year.
In 2022, the Federal Government introduced star ratings for aged care homes with the aim of providing simple, reliable information about the quality of care. Yet a new report suggests that instead of providing the transparency older people need to compare and choose an aged care home, the star ratings may actually lead them to choose a home that is delivering poor care. Rachel Lane reviews the report's findings.
Bitcoin has seemingly gone mainstream with approval for the first U.S. ETFs that can directly invest in the cryptocurrency. The question for investors is whether Bitcoin warrants a small allocation in their portfolios. Peter Lazaroff examines the pros and cons.
ASX REITs have been left for dead, some unfairly. Airlie Funds Management's Jack McNally sees Charter Hall Group (ASX:CHC) as a case in point. He says the company has a stellar track record and its 2024 profit guidance is conservative and likely represents trough earnings. Combine that with a large discount to asset value, and the stock appears great value.
With markets having gone gangbusters over the past six months, it's no surprise that the well-known Fear & Greed Index, used to gauge the current mood of the market, shows that it's now close to ‘extreme greed’ mode. Jonathan Daffron says investors are underpricing risk and it's time to get cautious.
Tony Dillon has been doing some light holiday reading by boning up on Albert Einstein's Relativity Theory. Rediscovering his 'inner physics geek', Tony sees several metaphorical parallels between the theory and the world of finance.
Two extra articles from Morningstar for the weekend. Johannes Faul looks at whether Kogan's shares are still attractive after a recent price surge, while Nathan Zaia does likewise with Judo Capital after its bounce post results.
Lastly, in this week's whitepaper, Magellan looks at global infrastructure investment and the positive prospects for utilities.
***
Weekend market update
On Friday in the US, a modest pullback halted the S&P 500’s five-session string of fresh closing highs, as the broad index gave back an early push higher to finish slightly in the red. Meanwhile, the Nasdaq 100 again lagged to settle 1.5% below its Wednesday lunchtime levels. Treasurys saw some softness at the short-end as two-year yields climbed higher by six basis points to 4.34%, while the long bond remained unchanged at 4.38%, WTI crude climbed above US$78 a barrel and gold stayed at US$2,018 an ounce.
From AAP Netdesk:
The local share market on Thursday extended its winning streak to a fifth day, hitting its highest close since the opening session of 2024. The benchmark S&P/ASX200 index finished up 36.2 points, or 0.48%, to a three-week high of 7,555.4. The broader All Ordinaries rose 37.1 points, or 0.48%, to 7,785.2.
Miners outperformed for the second day running.
Iron ore futures rallied after China's central bank announced it would cut the reserve ratio requirement - which is used to control the supply of money in the economy and influence interest rates - by 0.5 percentage points. BHP gained 1.5% and Rio Tinto lifted 2.8%. Fortescue Metals climbed 2% after the Andrew Forrest-led company reiterated production guidance for fiscal 2024.
Mineral Resources jumped 7.1 per cent after the lithium miner kept volume and cost guidance unchanged, saying all assets remain profitable despite subdued ore prices.
Domino's Pizza plunged 28.5% to a four-year low after the fast food chain withdrew its guidance for financial year 2024 amid a slump in sales in Asia and France.
Oil and gas giant Santos climbed 0.8% after announcing its troubled Barossa gas project would require an extra $200-$300 million in capital expenditure after it was delayed by a court trial brought on by traditional Tiwi owners.
ResMed soared 6.4% higher after the sleep apnoea device manufacturer beat analyst earnings expectations for the December quarter.
The big banks were mixed, with CBA up 0.1%, ANZ 0.3% and Westpac 0.6%, while NAB dropped 0.3%.
Curated by James Gruber and Leisa Bell
Latest updates
PDF version of Firstlinks Newsletter
ASX Listed Bond and Hybrid rate sheet from NAB/nabtrade
Monthly Bond and Hybrid updates from ASX
Listed Investment Company (LIC) Indicative NTA Report from Bell Potter
LIC Monthly Report from Morningstar
Plus updates and announcements on the Sponsor Noticeboard on our website