At the 2023 Sohn Investment Conference in the US on 9 May 2023, Duquesne Family Office CEO Stanley Druckenmiller spoke about the US Federal Reserve’s actions in the last two years and its impact on investing conditions. The entire interview went for over an hour, but we have selected these highlights.
***
I (recently) read Edward Chancellor's The Price of Time. As you know, I've been saying for years that my observation was the worst economic outcomes tended to follow asset bubbles. I was only looking at the past 100 years or so. Chancellor's book is a real tour-de-force, and it describes how this has been going on for over 500 years. Basically, every time we've had interest rates below 2% going back 500 years, it's been followed with a difficult economic time.
I think it was actually just a little over two years ago, I went on national television and said we had monetary policy that was the most reckless and extreme relative of the economic circumstances I had ever seen. And at that time, inflation was 2.5%. You had a booming economy, we're coming out post-COVID and it was clear post-vaccines that we were on our way to maybe the most rapid recovery I have seen in my lifetime.
I was not surprised about a year later when inflation reached 9%. I was not surprised that SPACs went crazy, Bitcoin went crazy, Dogecoin went crazy, equities went crazy. What I was surprised by was that for the next year, while all that happened, Jerome Powell’s Fed (Federal Reserve, the US central bank) continued to have their foot on the gas, they continued to buy US$120 billion of bonds a month while rates were zero. This obviously led to everything I just described.
Then realising they have probably made the biggest mistake in the history of the Fed, they slammed on the brakes. They raised rates 500 basis points (5%) in the last year. We know historically, two things happen.
Number one, the worst economic outcomes tend to follow too easily-engineered asset bubbles. And number two, big maxim in my business is Don't Fight the Fed.
So I'm sitting here staring in the face at the biggest asset and probably the broadest asset bubble - forget that I've ever seen that I've ever studied - and it went on for 10 or 11 years and then as the grand finale the government spent US$5 trillion on COVID and the Fed financed 60% of it.
(Editor note: As an example of a broad asset bubble, consider this chart, sourced from Multpl, of the S&P500 Price to Book Value ratio. It has only been higher in this period during the dotcom era of 2000 and the Fed-induced free money and loose monetary policy until 2022. Book value is the company's value in its financial accounts determined by subtracting its liabilities from the value of its assets. This exuberance comes at a time of rising interest rates, recession threats and tightening of bank lending).
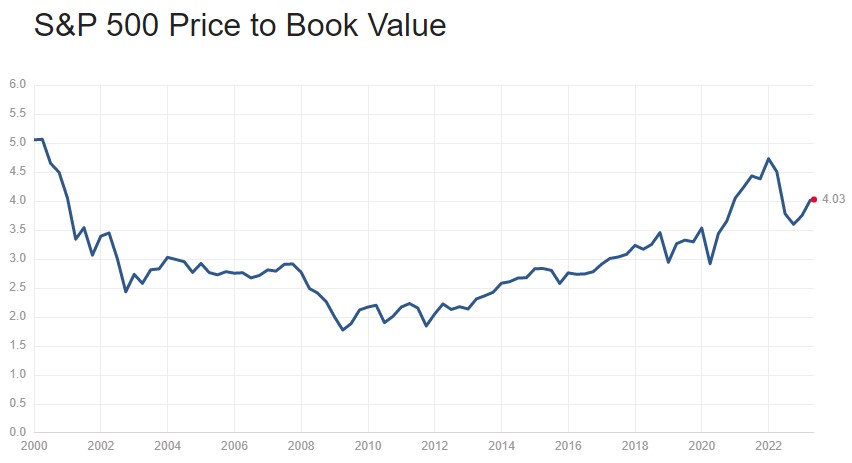
As I just described, now we have a big hike in interest rates. It's hard to look at that constellation of factors, know that we've only had a few soft landings since 1950 and all of them were preceded by what I would call proactive rather than reactive Fed policy, and believe we're going to have a soft landing. One never knows. But if you're just looking at the odds, they're very tough. In terms of the timing, I have left much less certainty on that than I do on whether we're going to have a hard landing or a soft landing.
The timing is difficult, but I will say in our shop we tend to use anecdotal information a lot. It's somewhat mixed. Housing, which has tended to lead historically, is actually fairly robust. Travel and restaurants and stuff like that are fairly robust. But trucking, which has been a guiding light for my firm in terms of economic forecasting with a six-to-eight-month lead time, is extremely weak. We're hearing bad anecdotes from retail. The banking problem we always knew.
Given what I've already described, there were going to be bodies out there. When you have free money, people do stupid things. When you have free money for 11 years, people do really stupid things. So the stuff under the hood is starting to emerge. Obviously, the regional banks recently, we had Bed Bath & Beyond. But I would assume there's a lot more bodies coming. The median regional bank has 43% of their loans in commercial real estate, about 40% of that in office. We've had this huge change in lifestyle due to COVID. Number one, the great resignation and number two people aren't going to the office. So we have actually a higher vacancy rate than we had in 2008.
I put all that together and I look also at the inverted yield curve. The timing is sort of third, probably fourth quarter of this year, first quarter of 2024. I wouldn't be surprised if the bean counters a year from now - as they tend to do backward looking - that things started (to go bad) sometime in the second quarter.
Stanley Druckenmiller is Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of his Duquesne Family Office. He made his reputation as an astute asset manager from 1988 to 2000 when he was lead portfolio manager for George Soros's Quantum Fund. The full Sohn Conference interview is linked here. This extract is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.