Some investors worry that regulatory tightening in China could strangle growth in its private sector, which is now dominated by technology companies and e-commerce platforms. Such concerns have wiped about USD1 trillion off valuations on China’s stock market over the past year. The poor sentiment has spilled over to other Asian markets and their tech sectors.
Why is China taking the risk of damaging these new drivers of economic growth when building a high-tech economy is part of its ‘common prosperity’ policy framework? Is there evidence of China’s regulatory overdrive negating investment incentives in its private sector?
How badly damaged is the private sector?
Many players see Beijing’s regulatory campaign, which started in 2020, as a move to exert greater control over the private sector and the technology firms and make them subservient to the Communist Party under the guise of an anti-monopoly policy. According to this school of thought, the survival of China’s private sector is under threat.
On closer examination, though, the e-commerce and technology companies subjected to the crackdown are a small share of the large and growing private sector. We have found no evidence of significant damage done to the private sector despite media reports to the contrary.
Reflecting the continued growth of the private sector is:
- The sharp decline in state-owned enterprises (SOEs) as a share of total industrial firms (Exhibit 1)
- The strong increase in private-sector employment in the industrial sector (Exhibit 2)
- The significant rise in the share of private investment at the expense of the SOEs’ share (Exhibit 3).
All this suggests that the large private and tech companies hit by Beijing’s measures play a small part in the overall private sector. While they may have made the news headlines, their situation is not representative of the whole private sector.
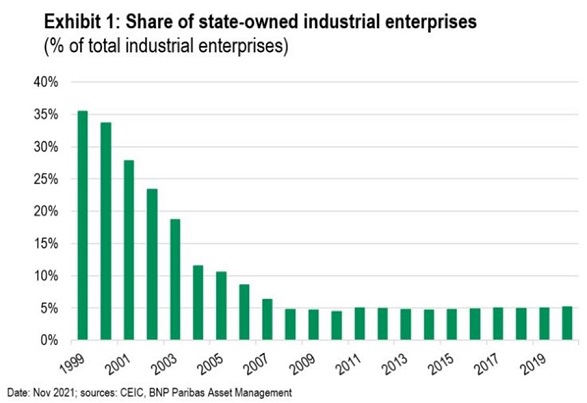
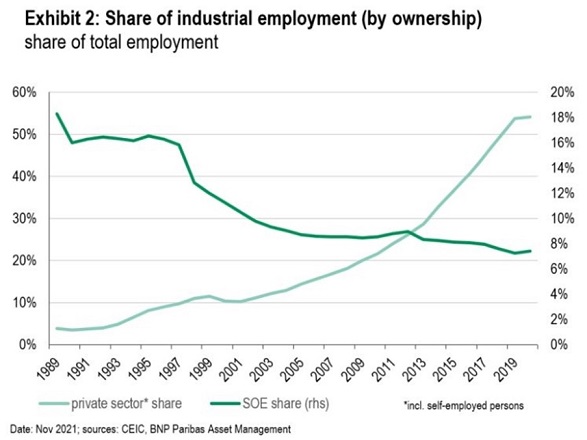
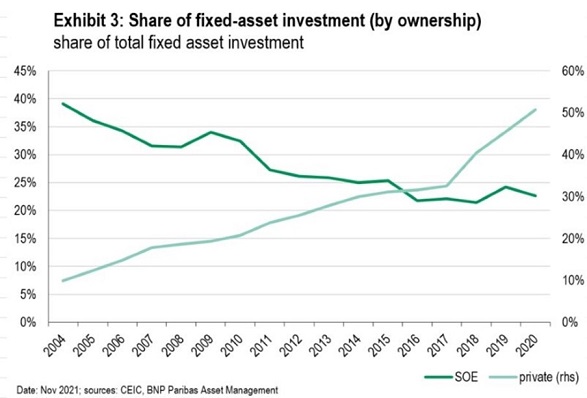
We have also found no evidence as yet of the much-feared decline in private investment in the wake of the regulatory tightening.
High-frequency investment data shows that while the growth rate of fixed asset investment by non-state-owned companies [1] has slowed, it has continued to outperform SOE investment by a wide margin since the regulatory campaign began (Exhibit 4). In fact, SOE investment has been contracting since early 2021, while non-state and private investments have continued to grow.
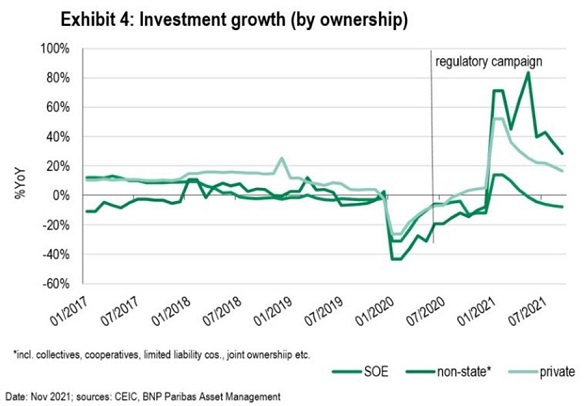
Why the crackdown?
Beijing is taking the opportunity arising from the economy’s Covid recovery to tighten oversight. It aims to align the private sector’s interests with Beijing’s strategic targets. Indeed, such reform is long overdue, as poor oversight has allowed many Chinese private companies, notably the internet firms, to prosper and add to moral hazard problems in the system.
Granted, China needs proper regulation for its private and tech sector. The question is whether it has now over-tightened and, thus, risked strangling innovation and incentives in the private-sector. This concern has understandably spooked markets, leading to a sharp sell-off in Chinese equities, especially tech and e-commerce stocks.
However, we believe China is just catching up with global practices of tighter supervision of tech companies rather than pursuing a more aggressive agenda to rein in corporate profits or destroy private capital.
Evidence shows that other countries, notably the US, the EU, South Korea and Japan, have been active in probing technology firms for alleged collusion and monopolistic practices and bringing anti-trust cases against global tech companies. [2]
What makes China different is that it has stepped up tightening efforts on the internet sector faster than other countries. An examination of Asia’s new regulations and remedy measures suggests they are broadly in line with those implemented by Europe and the US. [3]
For example, Chinese anti-trust laws allow for fines of 1-10% of annual turnover for anti-monopoly violations. This is consistent with most practices around the world. However, China and most Asian countries have been lagging in implementing the laws. They are catching up now and China has become even more active in enforcement.
Market implications
In a nutshell, China’s regulatory tightening since 2020 is, arguably, a tactical shift of its reform policy under the ‘dual circulation’ framework to tackle intensifying domestic and geopolitical challenges. Beijing still wants the private sector to drive innovative change and fund the development of high tech.
The regime change may have been abrupt, hurting the valuations of some of the best-known private companies and unsettling the stock market. However, the resultant correction now appears to have priced in most, if not all, of the regulatory concerns.
Repricing the internet sector under the new regime should give China’s tech sector a new investment horizon when the dust has settled.
Chi Lo is the Senior Market Strategist APAC of BNP Paribas Asset Management based in Hong Kong. The information published does not constitute financial product advice, an offer to issue or recommendation to acquire any financial product. You will need to seek your own advice for any topic covered in the article.
[1] Non-state-owned firms include private firms, collectives, cooperatives, joint enterprises, foreign private firms and sole propriety ownership.
[2] “A Cheat Sheet to all of the Antitrust Cases Against Big Tech in 2021”, Quartz, 29 September 2021 at https://qz.com/2066217/a-cheat-sheet-to-all-the-antitrust-cases-against-big-tech-in-2021/.
[3] “APAC Regulatory Fears Drive US$1tn Selloff: Overreaction or Signal of More to Come?” UBS Q Series, Global Research, 20 October 2021.