August 2021 marked the longest run of consecutive positive months for the Australian share market since World War II. Although such long positive runs are unusual, they are by no means an automatic warning of imminent demise. Previous long positive runs for shares were not all followed by crashes or corrections, at least not immediately thereafter. However, the current run may end in September as healthy dividends leave company bank accounts.
A strong sign of confidence
This particular measure is rather fickle, as a sustained run of positive (or negative) months can be broken by a miniscule negative (or positive) month caused by something which might be a completely random event. However, it does provide a general picture of overall market sentiment and confidence in the form of sustained bouts of optimism (or pessimism).
The main chart shows the steady upward march of the local share market over the past 150 years through booms and busts along the way. The lower section shows the runs of consecutive positive months (green bars) and runs of consecutive negative months (red bars).
Most of the time, the market drifts along, switching between short runs of up to three months at a time up or down. Every few years a more sustained run develops, and these are highlighted in the chart.
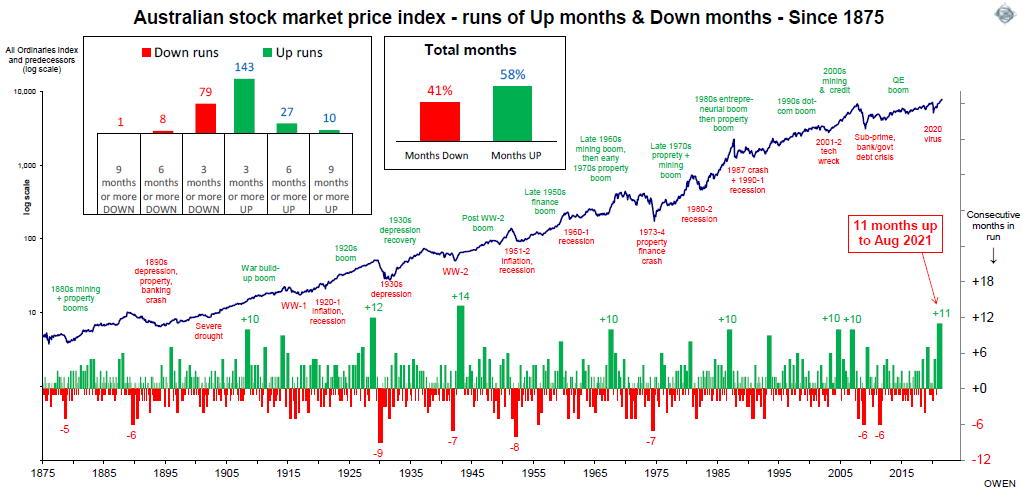
The longest positive run for shares in Australia was 14 months from April 1942 to September, 1943, when the market rose by 30% in the middle of World War II. Prior to the run, the market had fallen by -29% from September 1941 to the end of March 1942. The turning point for the War in the Pacific, and the trigger for the start of the share rebound, was General Macarthur's arrival in Australia as the Supreme Commander of Allied Forces.
The 14-month share rally was ended not by a correction but by a tiny -0.1% fall in October 1943, and prices then kept on rising more or less steadily to the end of the War.
There have been several positive runs of 10 months for shares, including two during the 2003-07 China/credit boom, one in the mid-1980s takeover boom prior to the 1987 crash, one during the late-1960s mining/oil boom, and one during the post-Federation drought. There was also a 12-month positive run ending in May 1929 before the 1929-31 crash.
Negative runs fewer and shorter
On the other hand, runs of consecutive negative months for shares have been fewer and shorter than the positive runs. This is highlighted by the larger of the two insert charts in the main chart above.
The longest run of negative months was ‘just’ nine months from August 1929 to May 1930, when the broad market fell by -34%. That was essentially the first half of the -64% fall in the 1929-31 crash.
Australian company profits surging back
The tremendous run of 11 consecutive months of gains in the local share market is likely to come to an end this month (September 2021) but the reason is that company profits and dividends are booming, not falling.
Company share prices will fall as they pay out unusually large dividends from the very strong reporting season to the end of June. If a company with a share price of say $20 pays a $1 per share dividend, the share price will fall by the amount of the dividend (plus or minus any other impacts on the company or the broad share market that day). The ‘total returns’ to shareholders are unchanged. The shareholder’s wealth is still the same $20 per share: $19 in the market value of the share after the dividend is paid out, plus the other $1 now in the shareholder’s pocket.
As this season's dividends will be the largest in history, investors will need to take extra care to redeploy the extra cash into productive investments, because cash is still returning zero.
The good news is that the bumper profit and dividend picture is well ahead of the targets to recover from the 2020 collapse, although we are still in lockdown (and probably back in economic contraction).
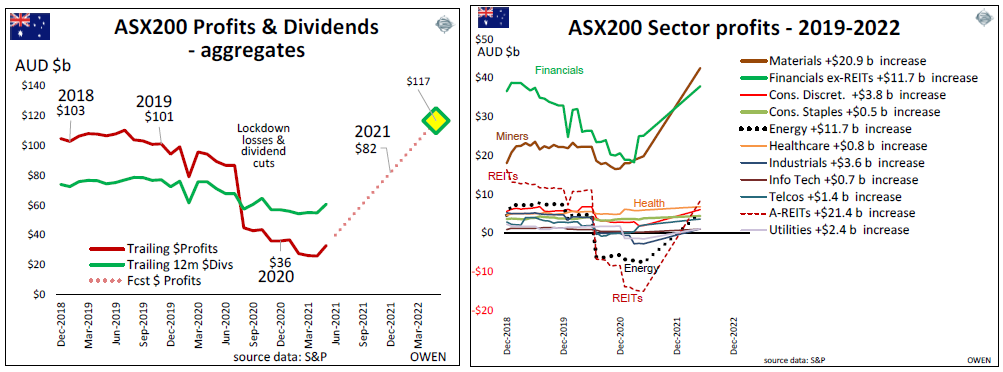
The next pair of charts are from our past reports to show the extent of this recovery. The left chart shows the steep decline in aggregate profits (maroon line) and dividends (green) in 2020, and it highlights the profit rebound target, high in the sky ahead. Aggregate profits fell by $101 billion in 2019 to just $36 billion in 2020 but were forecast to rebound to $82 billion by the end of 2021, and then $117 billion to June 2022.
These profit rebound forecasts have been keeping the share market rising over the past year. The magnitude and speed of the rebound appear ambitious at first sight, but we track it stock-by-stock and we have been confident that the rebound will be achieved or exceeded. The right chart shows the profit rebound targets by sector.
August is the main reporting season in Australia as most companies have June financial years. There are some significant exceptions, including three of the big four banks (ANZ, NAB and Westpac have September years), and most of the oil and gas majors have December years.
The US market (more than half of the global share market) has quarterly reporting whereas the ASX only requires half yearly, and the US and global markets are well ahead of target to more than fully recover their 2020 losses in 2021.
The iron ore bonanza
The right chart above shows the Resources sector of the ASX was targeting a profit increase of $21 billion over last year. It looks ambitious, but it has already been achieved – from just the three big iron ore miners – BHP, RIO and FMG.
The table below sets out their combined increases in profits ($22 billion) and dividends (also $22 billion) from the June 2020 half to the June 2021 half.
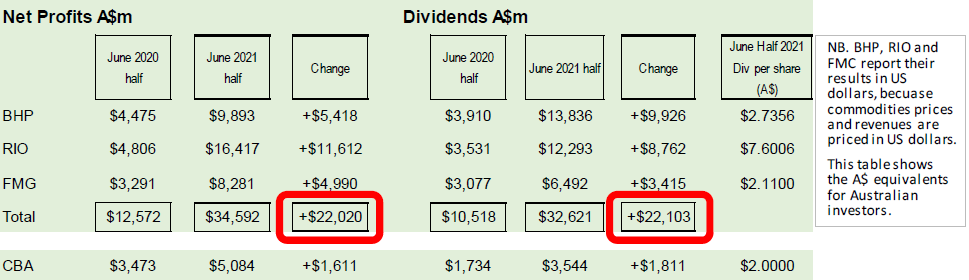
We also show CBA at the bottom of the table for comparison, as CBA is the largest stock in the ASX. CBA’s very respectable increases in profits ($1.6 billion) and dividends ($1.8 billion) over the same period have been dwarfed by the iron ore bonanza.
Ashley Owen is Chief Investment Officer at advisory firm Stanford Brown and The Lunar Group. He is also a Director of Third Link Investment Managers, a fund that supports Australian charities. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.