Give me time to realise my crime
Let me love and steal
I have danced inside your eyes
How can I be real?
Do you really want to hurt me?
Do you really want to make me cry?
Precious kisses, words that burn me
Lovers never ask you why
In my heart the fire is burning
Choose my colour, find a star
Precious people always tell me
That's a step, a step too far
- Extract from the lyrics of Culture Club’s, Do You Really Want To Hurt Me?
The wish to “Give me time" is unlikely to be granted by the Treasurer, Jim Chalmers, when the term of Reserve Bank Governor, Philip Lowe, finishes in September 2023. It’s more likely that “Precious people always tell me that’s a step, a step too far” is the Treasurer’s thinking, and there are many “words that burn me” in the Reserve Bank Review for the Governor to consider.
Large sections of the Review are devoted to the need for its leaders to drive institutional and cultural change away from a risk averse and hierarchical structure. Despite his obvious dedication and talents, someone who has been at the Reserve Bank for 43 years and effectively ‘Chief Executive Officer’ of the ‘business’ since 2016 is probably not the best person to drive the change. It is not even clear who is responsible for monetary policy and running the institution:
“formal roles and responsibilities relating to risk governance are somewhat unclear, with responsibility split between the Governor, the Reserve Bank Board and the Payments System Board.”
Governor rejects criticisms of culture
Although Philip Lowe told a press conference on Thursday, following the release of the Review, that he was not taking its conclusions personally, he must have at least squirmed at parts of it. He has conceded and apologised for errors of judgement in the past, but he said last week that the description of the Board’s operations “didn’t really resonate with me”. On page 124 is an example of an important section he disagrees with:
“However, many consulted by the Review were concerned that the Reserve Bank Board as currently set up can provide only limited challenge to the view of the RBA executive. The Reserve Bank Board has not voted against a recommendation of the RBA executive in at least the last decade (RBA 2022g). Current and former Reserve Bank Board members themselves described the Reserve Bank Board’s role in various ways, ranging from providing real-time feedback on the economy, to an informed second opinion, to a ‘pub test’ of how decisions might be understood by the public. These explanations centred on the external members providing a non-expert challenge to the RBA executive’s proposed monetary policy approach. That leaves the underlying economic and financial judgements with insufficient external scrutiny or challenge and represents a missed opportunity.”
Lowe went further in underplaying the Review’s findings, and despite the extensive coverage the Review has received espousing the significance of the recommendations, he said:
“It’s not correct to say a different decision-making structure would make fundamental differences. We’re talking about improvements at the margin.”
Get that ... "at the margin'. He was supported by Reserve Bank Board member, Mark Barnaba, in an interview the next day, where he also said:
“Notwithstanding the length of the report and the number of recommendations, in substance the changes are more marginal than appear.”
It is tempting when opening the 294-page Review to go straight to page 17 and read the recommendations, but most of it is pedestrian. They include the familiar, such as “The RBA should continue to have operational independence for monetary policy”, many ways to explain decisions better and “continuing to …”. The most material change is the establishment of a separate Monetary Policy Board.
But then comes Chapter 4 on poor cultural practices at the Reserve Bank, and the real gravity of the Review is in the damning revelations of how Australia’s central bank operates. It is what is often described somewhat awkwardly as ‘culture’ that will hurt Lowe the most. From page 155 is devoted to addressing considerable shortcomings in culture and an attempt to define it:
“Culture is the shared values and beliefs that guide how members of an organisation approach their work and interact with each other (Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet 2019). It lies at the heart of how organisations work. Important drivers of culture include the structure, systems (including governance), organisational policies and leadership of the organisation. Strategy focuses the organisation’s actions and decision making.”
Do you really want to hurt me?
If there is one sentence in the Review which undermines Lowe, it is this:
“The Reserve Bank Board did not receive any written briefings proposing calendar-based forward guidance before it was introduced by the Governor in a speech in mid-October 2020.”
So the most consequential and often-quoted statements by the Governor about no increase in cash rates until 2024, which encouraged thousands of borrowers to buy residential property in the boom of 2021 and which he admits was serious error, had not received any written analysis by the Board. And yet the Reserve Bank Board then ran with it.
“This language was updated in February 2021: ‘The Board will not increase the cash rate until actual inflation is sustainably within the 2 to 3 per cent target range. … The Board does not expect these conditions to be met until 2024 at the earliest.’ The Reserve Bank Board maintained this calendar-based component of forward guidance until November 2021. It continued state-based forward guidance until May 2022.”
A close second in incriminating evidence is the lack of dissent and independent thought, and says the Review (p124):
“The Reserve Bank Board has not voted against a recommendation of the RBA executive in at least the last decade.”
There is no dodging how critical the Review is of the Reserve Bank leaders, and it places Jim Chalmers in a clear position. For example, on page 164 under the heading, “Greater delegation and empowerment of staff members”, it says:
“RBA staff members frequently raised decision making, delegation, and hierarchy as areas for improvement. The Review heard from staff members that decisions tend to be pushed up to or retained exclusively at more senior levels. Others relayed that delegation was inconsistent across teams or could change at short notice, creating risk. Staff members identified various drivers for this including:
- risk aversion, which in this context shifts accountability or blame for potential mistakes
- lack of clear accountability
- a culturally ingrained deference to authority
- incentives that reward individuals for analytical output and those who appear to be across technical issues, resulting in resistance among some managers to genuinely delegate and empower team members.”
Does an army of economists lead to better decisions?
Another recommendation about the new Monetary Policy Board is generating unwarranted excitement. Is there an expectation because more economists are involved in decisions, that some magic potion will be sprinkled over the Australian economy? This new Board will still wield only one extremely blunt instrument, interest rates, and there is little evidence that similar boards overseas made superior decisions in recent years.
In any case, the existing Board has three economics PhDs, two others with masters degrees in economics and another with financial economics. That’s six members of the nine-member Board with suitable qualifications, and hundreds of combined years in financial markets, as well as senior business executives. Plus support from 1,500 Reserve Bank staff including an army of well-qualified economists. The Governor and the Treasury Secretary will continue to sit on and guide the Monetary Policy Board and select the other members.
And on it goes. Another recommendation is: “The Monetary Policy Board should convene and engage with an expert advisory group on monetary policy.” And within the Reserve Bank itself, policy formulation should be improved by “establishing a monetary policy strategy team”. It’s becoming a cast of thousands. There is even “The RBA and Treasury should develop an Australian Macroeconomic Policy Research Program …”
How many experts opinions do we need? Or want?
Even within the Reserve Bank itself, there is criticism that the place is ‘run by economists for economists’. Staff members are quoted as saying:
“Many staff members remarked to the Review that the RBA has a long history of transferring professional economists from policy departments into senior corporate roles. A common remark the Review heard was that the organisation was ‘run by economists for economists’. Asked about what they would like to change about the RBA’s culture, staff members’ observations included: ‘There are economists everywhere in the Bank where they shouldn’t be, and their opinion is weighed higher than all others. Employing them removes the opportunity for subject matter experts to actually improve and innovate.’ ‘I think there is a fundamental bias in the RBA’s culture to promote economists even though there are staff who have years of operational experience. Due to this, I’ve seen operational staff with a lot of corporate knowledge leave the bank.’”
Another consequential recommendation is that the Monetary Policy Board should communicate more frequently than the current Board. For example, Recommendation 10 is headed “Strengthen monetary policy transparency and accountability". It includes steps for the Governor to present to the public more often, such as:
“The Governor should hold a press conference after each decision meeting to explain the Monetary Policy Board’s view of policy and economic developments.”
and
“External Monetary Policy Board members should be expected to discuss the decisions and thinking of the Board publicly, including through at least one speech or public engagement a year.”
Philip Lowe already makes regular speeches and most of them repeat previous points. I listen to or read all of them and the repetition of questions and answers and responses is tiresome, but that's not Lowe's fault. He says it's possible to communicate too much.
The major change is now we will know whether some Board members dissented (and it's likely that they will more often given the Review's criticisms of passive members), especially since they will be encouraged to make their own public presentations. That's eight other Monetary Policy Board members making at least one public speech a year each, plus all the Governor's announcements.
There will be so much content on interest rates out there that the market, investors and the public will be thoroughly confused. Or bored.
Changing the Reserve Bank culture
According to the Review, a complete overhaul of the way different opinions reach senior levels is required. The Review begs for a sweeping broom to come in from outside and completely change the hierarchy.
There are many comments on empowering staff and raising the dynamism of the organisation. The recommendations to improve leadership are critical, such as in Section 11.2:
- mandatory leadership training for all managers
- annual externally facilitated 360-degree feedback mechanisms for managers with subsequent leadership coaching services
- ensuring its leaders are assessed for how effectively they deliver performance management and development processes that capture both the business outcomes and how those outcomes were achieved.
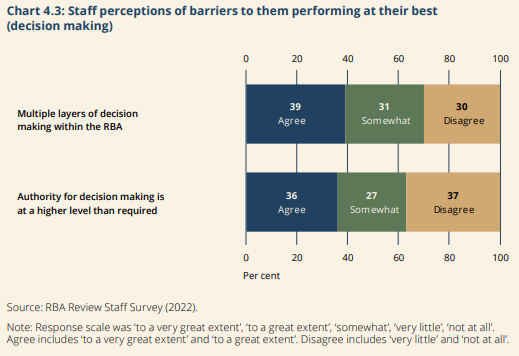
A survey of Reserve Bank staff revealed many consider there are significant barriers to them performance at their best.
Here is a selection of other quotations from the Review:
Page 39: “The evidence gathered by the Review suggested that there was not a sufficiently deep ongoing debate around the strategy of accepting gradual progress towards the Reserve Bank Board’s targets. The Board papers contained only limited consideration of alternative strategies, whether because the executive chose not to put them forward or the Board did not ask for this material.”
Page 43: “The Reserve Bank Board was not provided with, and on the available evidence did not demand, enough information in advance to fully debate and challenge the key design choices for the tools proposed by the RBA executive.”
Page 47: “In contrast to most of its peers, the RBA offered guidance over a long time-horizon and did not update its guidance as the economic outlook changed. This made the RBA particularly vulnerable to unexpected (positive) economic developments.”
Page 48: “The RBA projects that the cumulative financial cost of the bond purchase program to its underlying earnings over the next decade is likely to be large, at between $35 billion and $58 billion (RBA 2022b). The RBA provided information to the Review indicating that the cost of the Term Funding Facility is also likely to be large, in the order of $8 billion.”
Page 169: “Many staff members remarked to the Review that the RBA has a long history of transferring professional economists from policy departments into senior corporate roles. A common remark the Review heard was that the organisation was ‘run by economists for economists’. Asked about what they would like to change about the RBA’s culture, staff members’ observations included: ‘There are economists everywhere in the Bank where they shouldn’t be, and their opinion is weighed higher than all others. Employing them removes the opportunity for subject matter experts to actually improve and innovate.’ ‘I think there is a fundamental bias in the RBA’s culture to promote economists even though there are staff who have years of operational experience. Due to this, I’ve seen operational staff with a lot of corporate knowledge leave the bank.’”
The work starts now
There are so many details for the Government and the Reserve Bank to trawl through, including new committees, new programmes, changes in structure and cultural overhaul that an entire chapter is devoted to implementation. An effective date for new appointments is 1 July 2024, notably beyond the expiry term of the current Governor.
But on culture and leadership, the Review suggests immediate action in 2023:
“Priority recommendations for the RBA in 2023
Strengthen the RBA’s management, culture and operations (Recommendation 11), including appointing a Chief Operating Officer, implementing mandatory leadership training, assessing leaders on their promotion of challenge and debate, and establishing a monetary policy strategy team.”
So there’s no time to waste for the 1,500 staff of the Reserve Bank, and a bevy of new appointments, mainly aimed at the elusive goal of guessing an appropriate level of a blunt instrument.
Five years from now, there will be another Review, with much focus on whether the culture club was successfully changed to bring in fresh and new ideas. It will require a major overhaul with plenty of risks.
Do you really want to make me cry?
Graham Hand is Editor-at-Large for Firstlinks.