With co-author Zunjar Sanzgiri
Thematic funds were long viewed as esoteric, but not anymore. The ‘black swan’ event of the coronavirus pandemic proved to be a paradigm shift for thematic exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Burgeoning demand for funds focussed on environmental, social, and governance factors is a classic example of this. The outbreak of COVID-19 evoked investors’ sentiment toward disruptive trends and sustainable investing across the world, opening a long runway for growth for thematic ETFs.
What is a 'thematic' ETF?
Our definition of thematic ETFs is based on intentionality rather than fund holdings. To identify intentionality, we have relied on a combination of fund names (a strong indicator of intentionality) and information gleaned from prospectuses, marketing materials, index methodologies, and Morningstar's own proprietary data points (such as investment objective) where possible. We have limited our universe to equity ETFs and excluded other asset classes, most notably fixed-income ETFs.
Sustainable funds are included, provided they seek to capture a specific theme. This means that alternative energy funds, which aim to capitalise on the transition to a low-carbon economy, are included, but most broad ESG funds, which select a diverse group of stocks based on ESG scores, fall out of scope. Funds like the BetaShares Climate Change Innovation ETF (ERTH), which tracks a climate solutions theme, are included, but broad-based ESG-focussed funds like VanEck Vectors MSCI Australian Sustainable Equity ETF (GRNV) are excluded. The thematic funds taxonomy is elaborately noted in our latest Global Thematic Funds Landscape report.
The Australian thematic ETF market composes just over 1.7% ($1.9 billion) of the total ETF funds under management. However, the thematic market has seen a significant uptick over the trailing one year, with six out of a total of 11 Australian thematic ETFs launched during this period. This may reflect investors’ increased appetite for thematic investing.
Thematic ETFs, if chosen carefully, have the potential to complement an existing diversified portfolio with added alpha, but the risks are notable.
Setting expectations amid rapid change
Setting specific performance expectations from thematic funds is hard. Many strategies with more-esoteric themes have short track records, and distinguishing whether the underlying theme is really a transformational trend or simply the latest fad takes time. In the interim, factors like regulatory scrutiny, further technical advances, or a shift in investors’ collective psyche may result in an abrupt boom or bust of a particular theme. In either scenario, however, forming a forward-looking view on absolute or relative performance can be precarious. As such, thematic funds are not suitable as the main building blocks for a diversified, goal-focussed portfolio.
Is the juice worth the squeeze?
Thematic funds are designed to exploit emerging trends, not to provide diversified, risk-controlled exposure. They are concentrated in their respective sectors of interest and often rely on a relatively fewer number of stocks compared with the typical diversified offerings.
Exhibit 1 highlights these traits for Australian thematic ETFs. The risk of capital loss is high as sector- or industry-specific idiosyncrasies have a huge bearing on the performance of such funds. Adopting a passive approach in such scenarios can add more risk given the little (or lack of any) qualitative oversight. As a result, investors may experience a rougher ride due to higher levels of volatility.
Exhibit 1: Thematic ETFs are generally concentrated in a few sectors
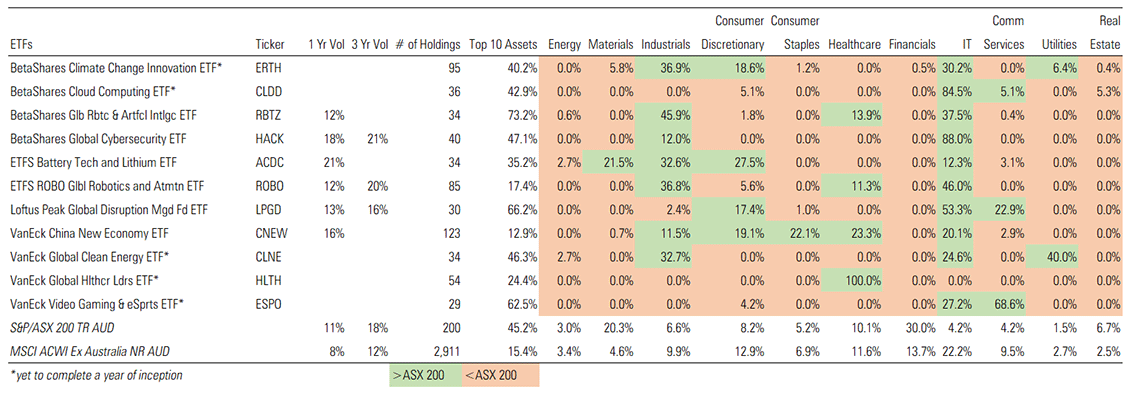
Source: Morningstar Direct
The higher risk exhibited by thematic ETFs naturally raises the question as to whether investors are adequately compensated for taking this risk. Our latest Global Thematic Funds Landscape report notes that over the trailing 15 years through May 2021, the risk-adjusted performance (Sharpe ratio) of the global thematic funds has been modest compared with pure passive ETFs.
Academic research such as Competition for Attention in the ETF Space 2021 by Itzhak Ben-David, Francesco Franzoni, Byungwook Kim, and Rabih Moussaon, corroborates these results. While the Australian thematic ETF market is at the nascent stage, they also exhibit similar global trends with either middling or, in some cases, worse risk-adjusted performance compared with passive ETFs like Vanguard Australian Shares (VAS) that offer broader market exposure.
Exhibit 2: Australian thematic ETFs have displayed global trend of modest risk-adjusted return compared with broad-based ETFs

Source: Morningstar Direct
Most thematic funds don't beat global equities over longer periods but since the beginning of the global pandemic, many thematic funds across the globe, including from Australia, have chalked up impressive returns. More than two-thirds of thematic funds globally survived and outperformed global equity markets (as proxied by the Morningstar Global Markets Index) in the year ended March 2021.
However, this success turns pale when longer periods are considered. For example, stretching the observation window to include the trailing five years, success rates drop to 43%. When viewed over the trailing 15 years, more than half of thematic funds globally have shuttered and just 22% have survived and outperformed the global equities benchmark. These figures suggest that the odds of picking a thematic fund that survives and outperforms global equities over longer periods are stacked against investors.
Crowding risk
Thematic strategies can also fall victim to capacity constraints. Theme-based investing frequently targets niche segments of the investment universe, which is often less liquid and less appealing from a valuation perspective. Too much money chasing too few ideas can stretch valuations and is not a recipe for successful long-term investing.
Exhibit 3: Compared with the broad market valuation, thematic ETFs’ valuations have been historically stretched on the P/E metrics basis versus the Morningstar Global Markets Index
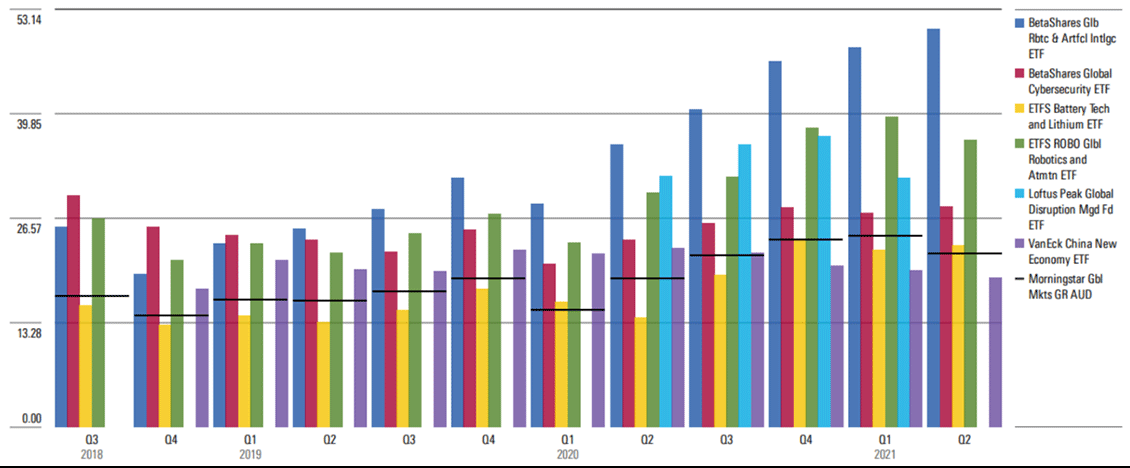
Source: Morningstar Direct. Note: Only ETFs with more than one year of data are considered here
What about the cost?
Thematic ETFs are not cheap relative to passive funds. While Australian thematic ETFs are in their early years, the trailing three-years data reveals that higher fees are being charged by these funds. This is a global phenomenon. The fees across the current cohort of Australian thematic ETF range from 57 basis points to 95 basis points (0.57% to 0.95%), which is substantially higher than their more-diversified peers.
Exhibit 4: Thematic ETFs charge substantially higher premiums for accessing emerging themes

Source: Morningstar Direct
Thematic investors not only pay a higher management fee but trading the thematic ETFs can be a costly affair, too. Exhibit 5 underscores the fact that the higher trading costs (gauged by bid-ask spread) mean a higher total cost of ownership associated with thematic ETFs. These higher spreads also point to the potential liquidity issues, specifically in stressed market environments.
Exhibit 6 shows data from research we published in February 2021 looking at spreads of all ETFs in a normal market environment (from 8 Jan to 20 Feb 2020) and in the stressed market environment during the COVID-19 market volatility (24 Feb to 3 April 2020).
Exhibit 5: Substantially higher bid-ask spreads of thematic ETFs compared with a broad-based ETF
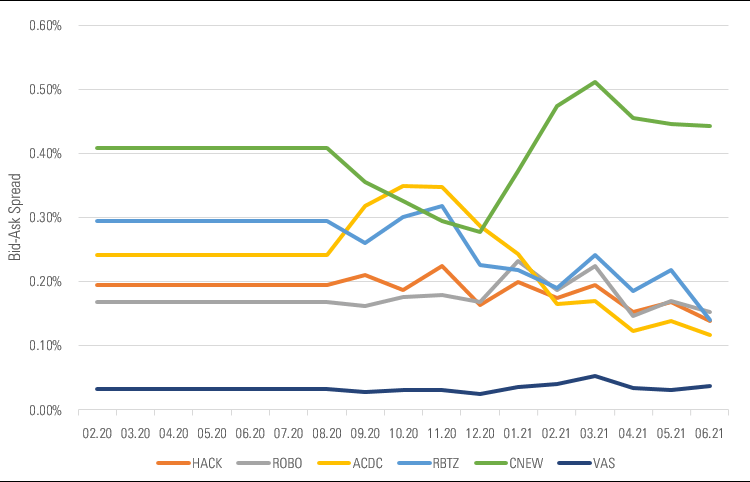
Source: ASX. Investment Products Monthly Update
Exhibit 6: Liquidity during normal and stressed market environments
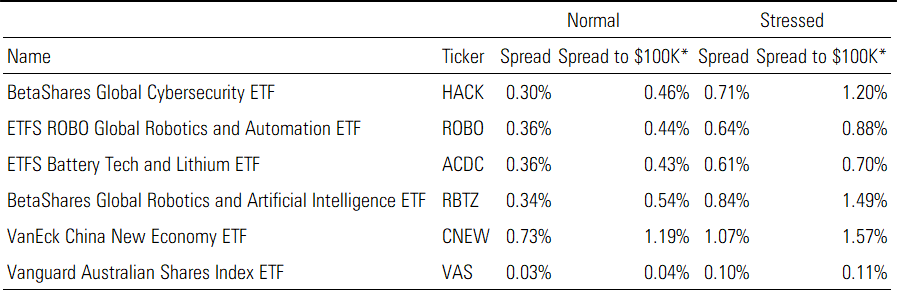
Source: Morningstar Tick Data. Normal Market: Data is from 8 Jan to 20 Feb 2020. Stressed Market: Data is from 24 Feb to 3 April 2020. Note: Only ETFs with more than one year of data are considered here. *Spread to $100K: Like the spread but calculated with the volume-weighted average prices derived from a notional $100,000 purchase or sale on either side of the order book. This spread is calculated only for periods where there is $100,000 in assets available on both sides of the order book.
Looking ahead
So how should investors approach thematic ETFs?
For starters, they warrant more in-depth research and due diligence than more-diversified funds. This is especially true because what is considered a theme can evolve through time and can become increasingly complex and nuanced.
In the case of an extremely specific theme, such as global food scarcity, the burnout rate can be high. Information technology is another such sector that is prone to perpetual changes. Once the flag bearer of the 'revolutionary tech' theme, giants like Facebook (FB), Alphabet (GOOGL), Netflix (NFLX), Alibaba (BABA), and Tencent (00700) (among others) no longer fit that definition following the 2018 MSCI GICS reclassification. As the fortunes of any theme are at the mercy of multiple factors - such as government policy, advances in technology, interest rates, and shifts in investors’ own biases - it is incumbent upon an investor to apprise themselves on the fundamental drivers of risk and return of the theme of their interest.
If a theme’s longevity is be established, it is critical for investors to identify the ETF which holds the companies that are most likely to benefit from the theme.
Thematic investing is tricky and involves multiple moving parts. It is crucial that investors understand what they own but this is particularly true when picking thematic ETFs, which come in a variety of flavours. Regardless of how certain an investor might be on a theme, we believe a thematic fund is best used as a supporting player to a diversified portfolio, as the performance volatility that may ensue could make it a 'roller coaster' of a ride. Thematic ETFs are best used to complement rather than replace existing core holdings.
Download the PDF version of this report, including Australian market-data snapshot as of 30 June 2021.
Kongkon Gogoi and Zunjar Sanzgiri are Senior Manager Research Analysts for Morningstar. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.