An international shipment of consumer goods typically comes with about 20 sets of documents, many of which are paper-based and relate to trade finance. About 70% of the information is replicated across the forms. This ‘red tape’ costs the freight industry hundreds of millions of dollars each year and has no real time visibility to all parties, is prone to errors and is often complex enough to delay payments.
No more, according to an Accenture-led syndicate. The consulting firm this year said it had a distributed-ledger solution that could “revolutionise ocean shipping” because it reduces data entry by 80%, simplifies amendments, streamlines cargo checks, and lowers the risk of compliance breaches.
Some observers said the innovation could be shipping’s biggest breakthrough since the first container ship sailed in 1956. The World Economic Forum says simplifying paperwork and other trade impediments “halfway to global best practices” could increase global trade by 15% and lift world GDP by nearly 5%, a greater boost than trade would receive if tariffs were to be abolished.
Distributed ledgers a potential revolution but with risks
Such is the promise of decentralised distributed ledgers that sequentially and immutably record and store data in a way whereby people have immediate access to the same information without having to pass through a central point. These ledgers are better known as ‘blockchains’, the software leap from 2009 that enabled the invention of cryptocurrencies.
Notwithstanding that cryptocurrencies are failing to fulfil money’s most central roles, especially to be a store of value, the blockchain rates as a landmark invention. Its innovation was that a self-sustaining network under no peak control allows strangers to make and accept payments over the unsupervised internet. And that’s the most apt use of the technology from a technical point of view, and pretty much it’s only widespread use so far, though much investment is underway to create blockchain solutions.
These distributed-ledger solutions for the regulated world, however, are likely to be less ground-breaking. Nonetheless, ledgers that are destined to be used in the regulated world could enhance productivity across many industries, even if they are not great advances on existing technology. A danger is that these ledgers will create risks, even systemic ones, when used in critical spheres. These risky uses include if they were used to replace paper-based voting in general elections because they are not tamper-proof, or if central banks adopt them for the monetary system at the risk of upsetting the fractional-reserve banking system.
Creating foundational technology
Future ledger innovations could be akin to blockchain’s development. A big hope is that ledgers can secure the internet’s protocols, the common agreements that enable devices to interact. Ledgers have this potential because they are considered a ‘foundational’ rather than a ‘disruptive’ technology – one that forms the basis of other milestone advances.
But distributed ledgers have drawbacks. These include privacy concerns, cybersecurity risks, that they require networks to be effective, their high power usage, their capacity limits – and there is always the risk that trust between users could break down.
The complexities in establishing networks and drawbacks in ledger technology mean the paperwork and multiple data entry that still exist after a generation of computer use are unlikely to find a ‘hey presto’ solution in blockchain form any time soon.
Worthwhile ledger solutions might only slowly appear in a regulated world as incremental advances on prevailing technology. That will make them valuable enough in a world in need of productivity growth, but only if their inappropriate use can be limited.
For those who are still getting their minds around blockchain, here's a simple illustration. More details are in the link below.
How blockchain works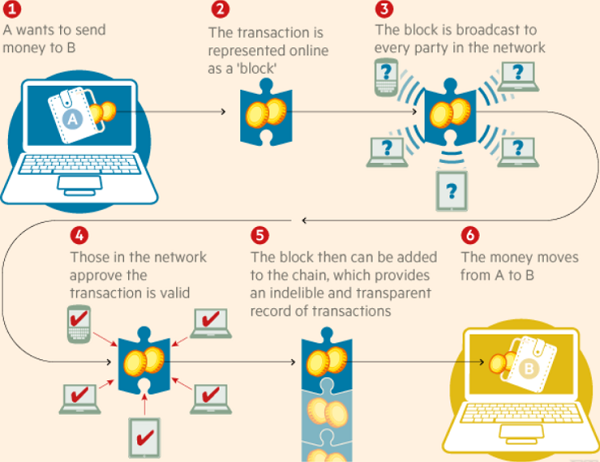
Source: Financial Times
Michael Collins is an Investment Specialist at Magellan Asset Management, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article is general information only, not investment advice. For the full version of this article go to: https://magellangroup.com.au/insights/blockchain-has-revolutionised-the-unregulated-cyberworld/
For more articles and papers from Magellan, please click here.