In today’s low interest rate environment where term deposit rates have remained sustainably low, investors have been attracted to the regular distribution payments and higher-return profile from hybrids. However, despite their many positive features, hybrids do carry higher risks versus Australian corporate bonds - which many investors don’t realise.
While allocating a small portion to hybrids can be effective, an approach highly focused on this asset class will pose problems. There are three primary risks to hybrids that will be explored:
- Hybrids historically have had a higher correlation to equity markets
- Hybrid debt issues are less frequent than Australian corporate bond issues
- Hybrids have significant call risk relative to Australian corporate bonds
Our suggested approach would be to adopt a diversified portfolio with adequate exposure to Australian corporate bonds alongside hybrids. Particularly in today’s environment, we place an emphasis on downside protection during market turbulence – like we have seen in the past few months.
There’s no doubt hybrids have a place, though the current returns from hybrids (especially financial hybrids) do look on the expensive side on a risk-reward basis. The yield to expected maturity/first call on bank hybrids are around 3-4% (unfranked). We believe five-year bank hybrids offer better value at around the 5-6% mark (unfranked).
1. Hybrids historically have had a higher correlation to equity markets
Over the GFC period, bank hybrids experienced close to a 20% drawdown (or price decline), which was primarily attributable to capital losses from the discount margins on these securities increasing from around 1% pre-GFC to around 5.5% post-GFC. Using this as a proxy for the current environment, if discount margins were to increase from the current 2.75% to around 5% over the next year, the capital loss would be around 6.5% offset by 2.75% income – thus, a drawdown of around 3.75%.
The recent experience for bank hybrids has been more muted. Bank hybrids are down by around 2-3% (in price terms) over calendar 2022 YTD compared to the ASX200, which is down by closer to 10%. On the other hand, the Australia corporate bond index has outperformed being down by around 1-2% (in price terms).
The GFC period was highlighted by:
- A fear of economic slowdown/banking crisis
- Protracted equity market weakness, and
- Large drawdowns (bank share prices falling by 20% plus).
The current sell-off is different in that it has revolved around higher inflation/higher interest rates alongside the Ukraine/Russia conflict.
The chart below gives a longer-term perspective of credit (or discount margins) for four types of credit investments: BBB rated bonds, US High Yield, CoCo (non-AUD, AT1/Hybrids), and Australian AT1/Hybrids). The last data point is 26 January 2022.
While BBB rated bonds do have some spread volatility (albeit, less so than AT1/hybrids), the bulk of the Australian corporate bond market sits in the A rating and above. A rated bonds have historically had very low spread volatility and risk-reward characteristics are better given potential drawdown risk.
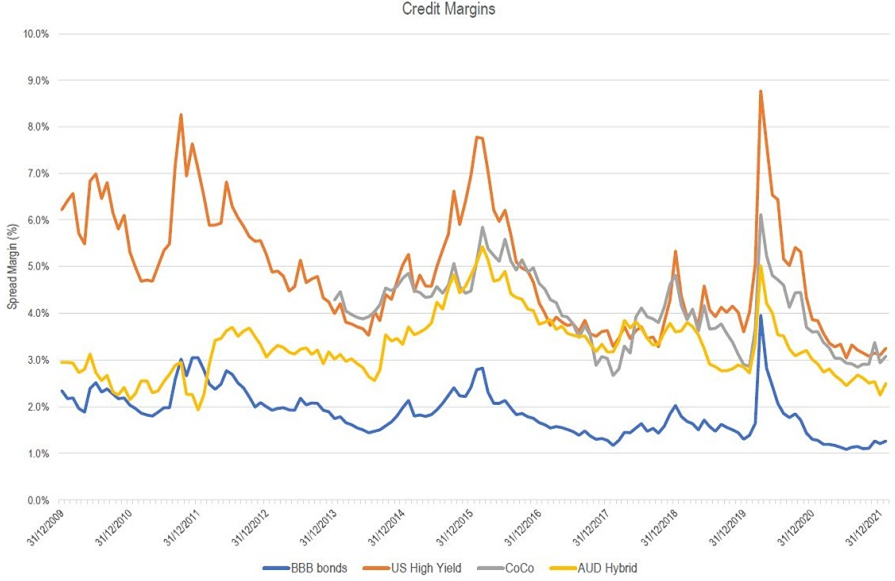
Source: BofA, ICE
2. Hybrid debt issues are less frequent than Australian corporate bond issues
The Australian corporate bond market has grown by more than 40% since 2010. Currently, there are over A$1 trillion Australian corporate bonds outstanding across governments, semi-governments, asset-backed securities, financial and non-financial corporates, inflation issuers, and hybrids.
However, the hybrid market is only a tiny segment of the Australian corporate bond market at around A$47 billion or 5% of Australian corporate bonds outstanding. Most of the debt issues are classified as ‘convertible preference shares and capital notes’ and issued from several financial institutions (mostly the major banks and Macquarie) – which also creates significant concentration issues with the Australian banking sector.
In years past, hybrids were also used by corporates (for example, Crown, Nufarm, and Qube) to obtain a level of equity credit for which to improve credit metrics. Rating agencies have since made this process more onerous on issuers, which, alongside issuers being able to get cheap funding from the corporate bond market, has seen a tailing off in corporate hybrid supply.
The issue hence becomes one in which investors can only get exposure to hybrids via the banks. As debt issues are less frequent in nature, replacement of capital then becomes very difficult, which poses reinvestment risk.
Generally, the hybrid market is also not a heavily secondary traded market – the number of trades per day is around 1,500 with a value of approximately A$700 million. For example, the bid-offer spreads (i.e., the difference between the market price at which the hybrids can be bought and sold) for CBA hybrid securities can be larger than those for its shares.
Australian Bond Segments
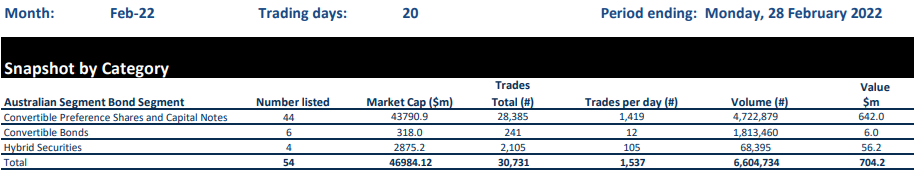
Source: ASX Hybrids monthly report, February 2022
3. Hybrids have significant call risk relative to Australian corporate bonds
The perpetual nature of many hybrids (especially the financial hybrids) means there is essentially no guarantee of getting your money back and thus no reliable yield to maturity (%). There are ‘reset periods’ with ‘reset margins’ but there is no end date for getting paid back. For this reason, investors are generally better placed to assess the running yield (%) for that period and then make a judgement as to whether they are comfortable or not.
Call risk also tends to rise in a higher interest rate environment as the issuer can hold onto old, low-rate hybrids rather than issuing new hybrids which have a higher rate of interest. Generally corporate bonds have a hard bullet maturity. All-else-equal, investors can be comfortable with the yield to maturity (%) on offer.
The other issue is that if a hybrid isn’t redeemed it’s probably going to be a result of wider market turbulence. So, if an investor wanted to exit, they’d be selling into the eye of the storm and potentially running into liquidity issues and realising a sizeable capital loss to do so.
Matthew Macreadie is a Credit Strategist at Income Asset Management, a sponsor of Firstlinks. To discuss this topic further and access corporate bonds please reach out IAM. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. Please consider financial advice for your personal circumstances, including eligibility for these investments.
For more articles and papers from Income Asset Management, please click here.