As non-classically trained investment operatives, we have found the basic question ‘Why?’ has served us well. In the past 10 to 15 years, watching market performance, we have constantly questioned why unlisted assets are expected to provide a return premium over their listed peers.
Classical investment theory defines the illiquidity premium as compensation for the loss of control (or liquidity) to exit an investment position at a desired point in time. This is sound logic if markets always trade upon fundamentals. Once behavioural forces come into play, this theory seems to deviate.
Locked funds versus loss of capital
Our research for this article left us thinking that the mortal sin of investing is having investors lose control of their equity in locked funds. While we appreciate the sensitivity of the loss of control, surely losing capital is worse. The distinction between these two will become clearer in a moment.
Historically, unlisted property has provided a return premium of between 100 and 300 basis points (1% to 3%) over listed property as recompense for poor or no liquidity. Property is a good asset class by which to assess the illiquidity premium concept as the listed and unlisted property markets in Australia are deep and generally well researched.
The figure below illustrates the returns from listed property and unlisted (core) property since 2004. This data captures the pre- and post-GFC markets, so represents the impact of the cycle.
Pre-fee cumulative returns, unlisted (core) and listed property (% pa, Jun 2004 = 100)
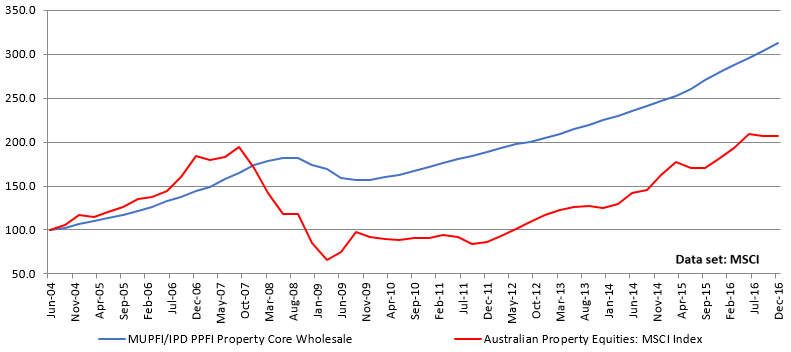
Source: MSCI
Listed market can suffer from liquidity
Pre-GFC, the listed market was trading at a premium to its unlisted counterpart, clearly at odds with the illiquidity premium, but the listed market was savaged during the GFC.
Herein lies the disconnect: in boom markets, the liquid market appears to trade at a premium to its unlisted counterpart, and then in a market correction, the liquidity sees prices savaged. Peak to trough, listed property lost ~70% of its value whereas unlisted property only declined ~20%.
There is an argument that liquid investors should obtain a premium for the price volatility of their investment. The listed market also took almost 10 years to regain its pre-GFC values whereas the unlisted space took just three years.
Consider our earlier point that losing capital should be the mortal sin of investment, not losing control of the equity. There were a number of unlisted funds that were frozen or locked during the GFC, which saw many investors lose the ability to manage their equity. While this is a less than optimal outcome, freezing these funds may have been the best preservation strategy for the equity at that time. Certainly, these charts indicate that being in an unlisted fund saw ~50% of the equity value preserved in the unlisted sector versus its listed peer. We consider that a reasonable outcome even when factoring in the loss of equity control.
The figure below illustrates year on year returns of listed and unlisted property markets. The listed market shows massive price volatility and ventures into loss territory three times, as opposed to the unlisted sector which has far more stable returns and ventures into loss territory only once.
Pre-Fee rolling annual returns, unlisted (core) and listed property (% pa)
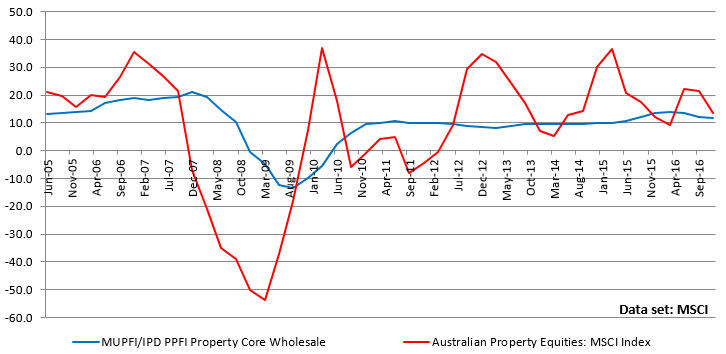
Source: MSCI
If the return expectation for a particular investment is a function of the risk the investor takes on, there is an argument that listed property should provide a return premium to compensate investors for the market risk during irrational periods (both bull and bear markets).
Reconsider the illiquidity premium
We are not pushing one position over the other. Rather we contemplate whether traditional thinking about the illiquidity premium may need to be reconsidered. Periods of exuberance or correction tend to see liquid markets surpassing the fundamental level of the underlying assets, both on the upside and downside.
On this basis, investors need to be clear as to why they are selecting one investment structure over another. Structural differences tied into the same asset class can provide divergent performance and therefore investors need to be clear about their objectives when taking a particular investment position.
Clearly, there are arguments for and against the illiquidity premium. Listed and unlisted markets both have an important role to play in investment portfolios, but the nature of each is shifting. Relying purely on classical investment theory when making asset allocations can be dangerous. As always, drill down into the data and see if the reality matches the theory.
Adam Murchie is a Director of Forza Capital Pty Ltd which provides property investments to high net worths, private clients and family offices. This article is general in nature only and does not constitute specific investment advice.