Rising inflation and official interest rates have helped to bring private debt into the mainstream of investment classes as investors seek to avoid the turbulence of public markets. The risk of a global slowdown is now also testing investment strategies.
Many investors are again looking beyond equities and fixed income to weather the economic uncertainty in a way that reduces capital volatility and maintains a reliable income.
For investors reliant on income from their portfolio, switching into bank deposits may be the first thing they think of. According to the latest SMSF quarterly statistics report (Dec 2022) from the Australian Tax Office, 16% of Australian SMSF capital is invested in cash and term deposits.
While this may be a well-worn path, it isn’t necessarily the best strategy for all trustees. Money in the bank does provide security but term deposits deliver lower returns that are locked in at a fixed rate and don’t keep pace with inflation.
Reduced capital volatility even during economic downturns
The global economy is in the midst of a broad-based slowdown, as the rise in central bank rates to fight inflation and Russia’s war in Ukraine continue to weigh on economic activity.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts global economic growth to fall from 3.4% in 2022 to 2.8% in 2023, before settling at 3% in 2024. The slowdown is expected to be especially pronounced in advanced economies, where growth is expected to slip from 2.7% in 2022 to 1.3% this year.
The IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook notes the global economy might appear poised for recovery but turbulence is bubbling below the surface. The situation remains fragile, as shown by recent instability in the banking sector, and inflation is stickier than anticipated even a few months ago.
As uncertainty around the economic and policy outlook continues, a key attraction of private debt is that it aims to provide capital stability through the economic cycle.
Australian corporate debt is a lower risk investment than equity because Australian corporate insolvency laws give priority to the interests of creditors in claims over the assets of a business.
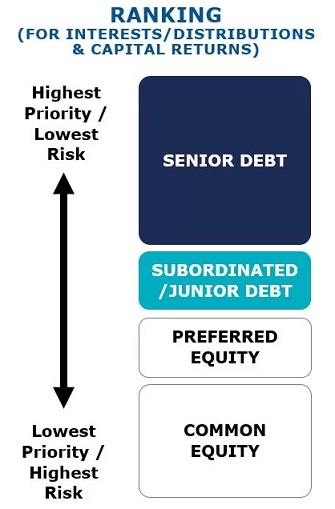
In a private market, lenders negotiate directly with borrowers, enhancing risk management. A skilled lender or private debt manager will negotiate with the borrower appropriate terms and conditions, controls, reporting obligations, covenants, and security to ensure the lender has greater influence on loan terms seeking to mitigate potential risk of loss.
Covenants and ongoing borrower reporting obligations are negotiated and provide protection and early warning of changing risks. Security held over the borrower ensures the rights and protection of capital ranks in priority to shareholder equity and any unsecured creditors.
Most loans in the Australian private debt market are senior secured loans. This means Australian laws protect the lender’s capital, giving them the ability to recover interest, principle, and fees from the assets of the borrower.
As a result of the protections in place, the corporate loan loss rates for Australian companies have been very low for many years.
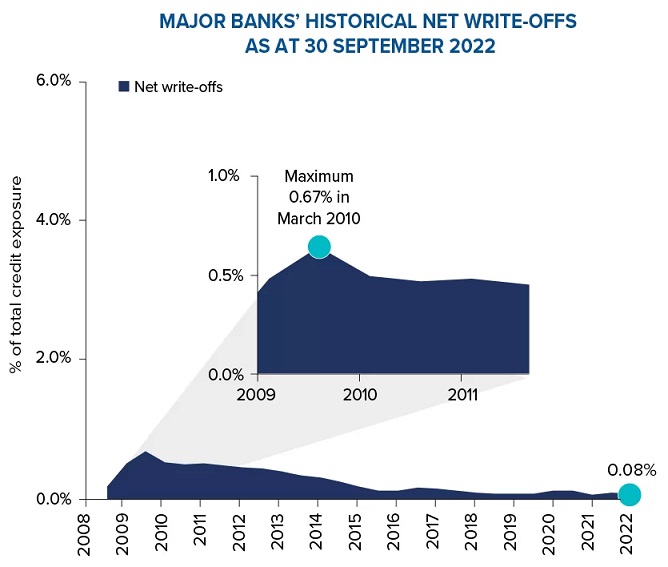
Source: Major Bank APS 330 reporting. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
Floating rate structure provides natural inflation hedge
While the economy is slowing, prices have accelerated. Global headline inflation rose to 8.7% in 2022 from 4.7% in 2021.
Central banks in major economies have tightened monetary policy rapidly to tackle this inflation but price pressures are proving quite stubborn. Global inflation is set to fall to 7% in 2023 due to lower commodity prices but is unlikely to return to target before 2025 in most cases, according to the IMF.
Inflation poses a threat to investors because it chips away at the purchasing power of savings and investment returns. It can be particularly damaging to returns on fixed income investments such as bonds.
Private debt offers protection against inflation because corporate loans earn their returns from fees charged to borrowers and interest that is generally charged at a floating rate. The interest on Australian corporate loans is usually structured as an additional margin over the benchmark Bank Bill Swap Rate (BBSW).
The BBSW is essentially the rate at which Australia’s major banks are willing to lend short-term money to other banks. It reflects not only the current level of the RBA cash rate but also the expectations the banks have of future cash rate settings.
So, if interest rates rise, income should also rise, which acts to protect capital.
Regular income even in turbulent times
Private debt can provide regular income, even during extraordinary times. Interest and fee payments are received from borrowers at specified intervals under the binding terms of their debt contract. A floating base rate, with additional credit margin, ensures total interest income rises in line with upward movements in market interest rates (which may occur as a means of combating inflationary pressure).
This contrasts with dividends that are paid to equity holders at a company’s discretion. Even when equity markets were at their most turbulent in early 2020 during the beginning of the pandemic, and many companies were suspending or reducing dividends, well managed private debt funds continued to deliver consistent monthly income for investors.
Attractive risk-adjusted returns
The private debt asset class can provide attractive risk-adjusted returns throughout the economic cycle. More conservative funds can deliver a return around 6-7%, an attractive alternative to low-yielding corporate bonds, hybrids, government bonds or even cash deposits. A higher yield fund can deliver a cash distribution around 10-12%.
Traditionally the asset class was only available to wholesale investors. However, in recent years, opportunities have become available to SMSFs and other self-directed investors to provide ways to access the opportunity in both listed and unlisted vehicles.
When accessing corporate loan investments through an ASX-listed structure (Listed Investment Trust or LIT), investors benefit from liquidity available via secondary market trading. Investors enjoy the premium income distributions associated with this asset class with the ability to buy or sell units on the ASX daily. When accessing private debt via an unlisted managed fund, investors are not subject to stock market volatility that may impact the LIT pricing and can buy and sell units in some funds monthly (subject to liquidity).
As one of the few asset classes that aims to provide capital stability as well as attractive, reliable returns, private debt can play a key role as investors seek to preserve and grow their portfolio at times of elevated uncertainty.
Andrew Lockhart is Managing Partner and Co-Founder of Metrics Credit Partners, an Australian debt-specialist fund manager, and sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor. Its listed vehicles operate under the tickers MXT and MOT.
For more articles and papers from Metrics Credit Partners, click here.