with contributions from Vanguard economist Beatrice Yeo
People in China went back to the movies this Lunar New Year, in a big way. Compared with 2019, box office revenues were up by a third at their 2021 holiday peak. These record sales came despite a 75% capacity limit imposed to counter a recent resurgence of COVID-19.
Daily life has largely returned to normal in China, the first country affected by the coronavirus. Because it contained the virus and its fallout better than most large economies, China could limit its fiscal and monetary support for the economy relative to others.
Signs of recovery
Still, policymakers, who even before the pandemic were tasked with balancing the nation’s growth and its financial stability, face a challenge in readjusting policy for more normal times. With China being the first major economy to emerge from the pandemic, and its growth having returned to its pre-pandemic trajectory in the fourth quarter of 2020, its policymakers’ moves will be assured a global audience.
Box office revenues provide anecdotal evidence of pent-up demand
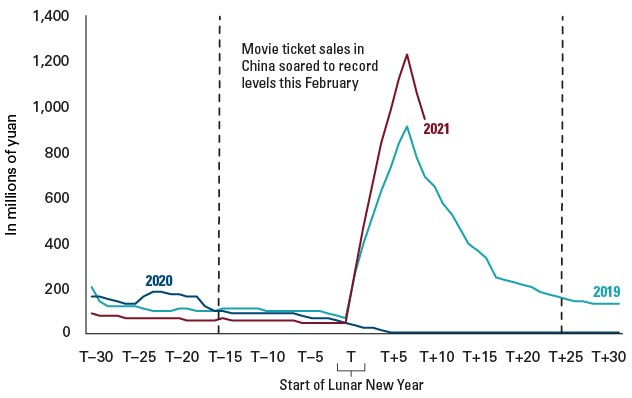
Notes: The illustration shows the seven-day rolling average of box office revenues in China. T represents the Lunar New Year, which this year was on February 12. Associated numbers represent the number of days before and after Lunar New Year. Data as of February 20, 2021. Source: Wind Economic Database. Data accessed February 23, 2021.
Other high-frequency indicators, such as those measuring container ship volumes and local traffic congestion, similarly suggest an economy that has largely returned to normal. China’s fourth-quarter 2020 GDP growth of 6.5% was greater than economists as a group had expected.
Although COVID-19 lockdowns interrupted China’s most important holiday period for a second year in a row, the economic effect this year was largely benign compared with 2020s. Whereas last year’s lockdown was nationwide, the lockdown that extended from late December 2020 through February 22, 2021, affected regions representing only 4% of China’s GDP.
The timing of last year’s lockdown left migrant workers stranded in their home villages, delaying restarts of factories after the holiday period. This year, lockdowns occurred before the holiday travel season, keeping workers in place and allowing for earlier factory restarts than usual. The resulting higher capacity utilisation in the industrial and construction sectors offsets some of the weakness in consumption and the service sector.
Vanguard recently published commentary on how monetary and fiscal policy remains a tailwind in most developed economies, where policymakers aim to sustain economic recovery and keep inflation expectations anchored.
In China, however, post-pandemic policy normalisation is a headwind.
Doubts about balance of growth and financial stability
For 2021, we expect slower credit growth, less government bond issuance, and a reduction in the fiscal deficit. The question is no longer whether and when the People’s Bank of China will normalise monetary policy - it’s the pace and magnitude of normalisation.
We expect tightening to be gradual and dependent on the economy’s performance. The recently released Jan-Feb 2021 economic data confirmed our expectations of accelerated production and exports offsetting the modest drop in consumption and investment, and reaffirms our forecast of sequentially slower but still positive Q1 growth forecast.
As both an emerging market and a global economic powerhouse, China faces a continuing challenge in balancing growth stability and financial stability. Rising leverage and housing market bubbles are among the concerns. I wrote recently about how China’s attempt to find such a balance may help explain a remarkable consistency in China’s official GDP numbers. A recent Vanguard research paper discusses an approach that we believe presents a truer picture of China’s growth.
But China also must find a balance between near-term and medium-term financial stability - a challenge shared by policymakers in developed markets. Policy normalisation that is too aggressive or not communicated well could trigger immediate stress in the financial system. We saw this play out in China with an interbank liquidity squeeze this January and credit-market stress in the second half of 2020.
In managing recovery from the unprecedented economic disruption brought on by COVID-19, policymakers in China and elsewhere will need to make sense of ever-changing data that at times will send mixed signals. To avoid undue market volatility that in turn could hamper economic growth, policymakers will need to communicate with markets effectively and stick to a well-prepared script.
Qian Wang is Chief Economist, Asia-Pacific and Beatrice Yeo is Economist, Australia in the Vanguard Investment Strategy Group. Vanguard Australia is a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.
For articles and papers from Vanguard, please click here.