In the age of the 24-hour news cycle, many are devoting considerable effort into predicting the next market move. However, history has shown that trying to ‘time the market’ is extremely challenging even for the most astute of investors. Given this, how should we think about investing and constructing portfolios?
A report by Research Affiliates titled 'Pricing Stocks and Bonds' introduces a simple framework which sheds light on how we can forecast expected returns and construct an optimal portfolio. Instead of focussing on the short term, Research Affiliates argues there is greater value in forecasting long-run returns which can be predicted with greater reliability. Admittedly, even forecasts of long-term returns are unlikely to turn out accurately. But precision in forecasting is not necessary for constructing optimal portfolios.
They illustrate this via a simple framework which has outperformed a standard 60/40 portfolio (60% equity, 40% bonds).
Simplest return expectations
In our quest to estimate future returns, a crystal ball is not needed to foretell the future. Instead, they attempt to quantify the returns if everything unfolds as they expect (which admittedly rarely happens). Hence, they account for returns from unexpected events through the idea of an ‘unexpected shock’. In short:
Future Return = Expected Return + Unexpected Shock
To establish the framework, they examine a scenario where everything plays out as they expect. Imagine investing in a security with zero chance of default, does not pay dividends and is held until maturity. An example of this is a three-month certificate of deposit. In this case, the future return of the investment and the expected return today is known with certainty as the purchase yield of the investment. They look up its yield and know exactly what the future return will be. They can consider the same problem in a different way by asking the four questions below:

If the answer to all of the questions above is ‘yes’, then they know with absolute certainty that the future return of the investment is equal to its yield today. Of course, most of the time, there is no certainty about future cash flows, either due to default (fixed income) or due to cash flows that are not contractual (e.g. equity dividends). As they attempt to price a wider variety of investments, they begin to answer more negatives to these four questions. Consequently, the expected return moves away from the purchase yield and returns becomes more difficult to estimate. To overcome this, they adopt a framework based on long-term expectations.
Begin with a focus on the long term
To minimise the impact of idiosyncratic shocks in asset returns, they focus on long-term returns as they tend to be more predictable. One study found the volatility of 1-year returns to be 19.2%, while the volatility of 10-year returns was only 4.7%. However, unless the historical average of returns is accepted as the future expected returns, a tighter distribution of returns is of no great use. Instead, Research Affiliates documents below how to forecast expected returns.
1. Forecasting bond returns
Calculating an asset’s expected return is dependent on assumptions of certainty, size of cash flows, reinvestment rate, and holding horizon. Relaxing the hold-to-maturity and constant reinvestment rate assumption, they find that a strong relationship exists between the yield of a bond today and the yield of a similar bond issued a year ago. As a result, they use knowledge of bond yields today to predict future bond returns even if they do not hold the bond until maturity.
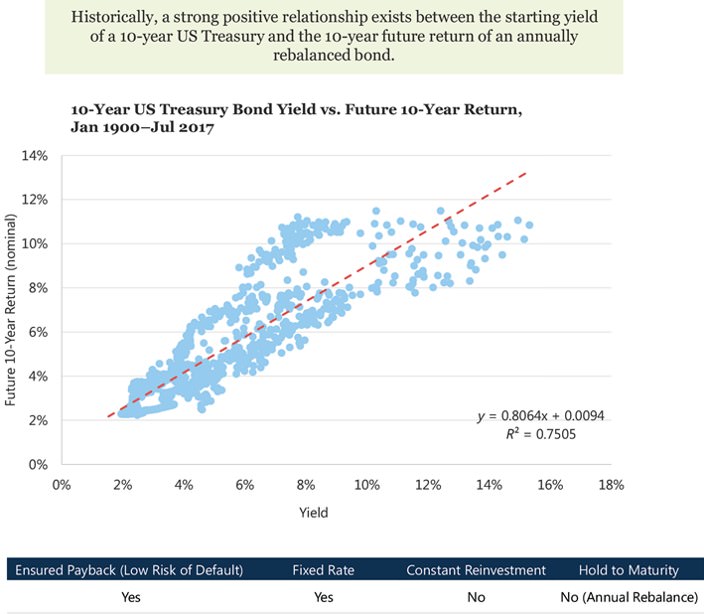
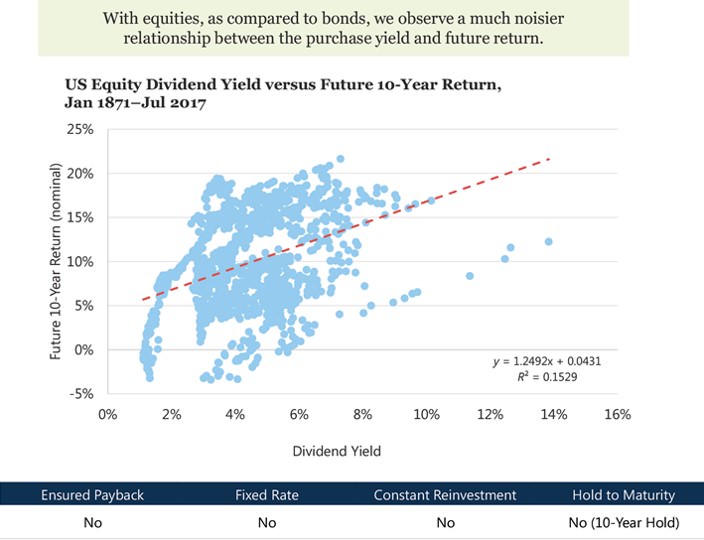
2. Forecasting stock returns
Forecasting stock returns is similar to forecasting bond returns, but they need to relax all four initial assumptions. This is because dividend payments are not fixed, equity holders can be wiped out by default, reinvestment rates change, and stocks do not have a maturity date. By relaxing these assumptions, dividend yield alone does not do a good job of predicting future returns. Instead, returns can be explained by three additional factors: inflation, growth in dividends and changes in valuation levels. The impact of these factors on returns can be seen below:
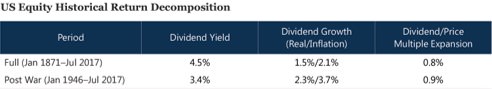
Research Affiliates finds the model does a fairly good job of predicting stock returns, however they concede they have often missed the mark. Forecasting returns is not an exact science.
Building a portfolio using expected returns
Using the expected returns generated, they proceed to construct a portfolio.
They allocate between stocks and bonds by comparing current expected return for each asset against its historical expectations. By doing this, they can form a ‘confidence score’ for stocks and bonds and allocate across these assets accordingly. For instance, if stocks have a high expected return versus its historical expected return, the model shows more confidence in the ‘cheapness’ of stocks and assigns a greater weight to stocks.
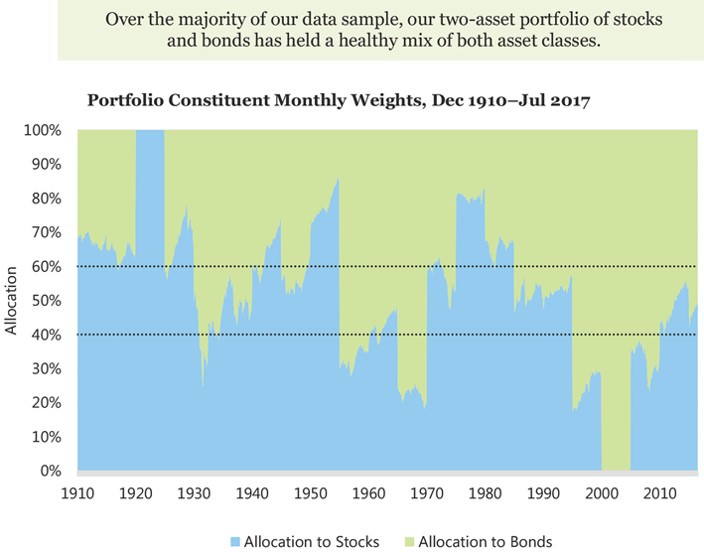
Using the strategy proposed, they find that it consistently outperforms a 60/40 portfolio across different rebalancing intervals, delivering superior returns with less volatility.
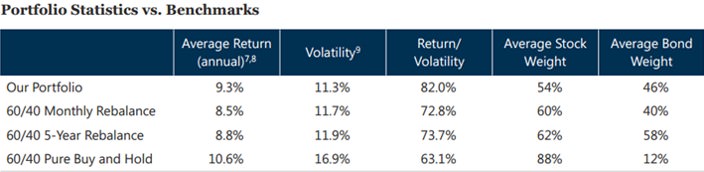
What this means
First, the framework does not imply they can predict short-term market moves. Instead, it focusses on long-term relationships that are more reliable.
Second, the proposed multi-question framework provides a useful approach for forecasting the future returns of any asset class. It is not limited to just stocks and bonds.
Finally, even if the long-term return expectations are not accurate, Research Affiliates argues they can construct portfolios which add value over a ‘set and forget’ portfolio.
Wilbur Li recently completed his Bachelor of Commerce (Honours in Finance) at the University of Melbourne and he will soon commence at a Melbourne-based fund manager. He has worked at Unisuper (global equities) and PwC (debt and fixed income). This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.