Investment in fixed income is often seen as a residual allocation, made only after an equity and property portfolio has been painstakingly constructed with sector and style diversification closely scrutinised. However, the performance of various fixed income instruments in March and April 2020 clearly shows that the same level of discernment is pivotal when making fixed income allocations.
While the medium-term outlook remains highly uncertain, now is a good time to undertake the detailed work needed to understand which securities and funds have performed to expectations, and those which have seen existing risks magnified or in some cases new risks brought to light.
For investors with a medium-to-long-term outlook, and a preference for income and liquidity, the good news is that the current market is creating opportunities to reimagine defensive asset allocations, which may include quality corporate credit.
Why corporate credit?
An index-unaware, actively managed and globally-oriented corporate bond portfolio offers several advantages:
- First, detailed credit analysis ensures that all holdings adhere to strict selection criteria aimed at avoiding defaults. Even a well-diversified portfolio can be significantly impacted by an issuer that does not meet its obligations.
- Secondly, interest rate risks and credit spread risks can be managed to reduce volatility of returns over time. While coupon income is the dominant source of return from corporate bonds, funds with the flexibility to adjust exposure to interest rates and credit spreads can more effectively manage risk in real-time and ideally also use skill to generate additional investment return.
- Finally, because issuers offer bonds in multiple currencies, an active manager can seek out the best relative value regardless of the currency. Implemented consistently over time, this flexible approach can lead to incremental return improvements.
Whether they be traditional managed funds or listed high yield bonds, Australian investors have never had a wider range of investment options when it comes to fixed income. Most recently, Listed Investment Trusts (LITs) have provided access to the global 'high yield' market for corporate bonds with credit ratings below investment grade. Offering attractive yields, they were enthusiastically adopted by retail investors.
However, the COVID-19 crisis has revealed the Achilles Heel of LITs - the ability of the unit price to trade below the underlying value of the assets (of course, they may also trade above the underlying value but this has not been evident in the recent crisis). Compared with other fixed income options, LITs have displayed equity-like volatility, although distributions continue to be paid. The longer-term risk is that these valuation discounts persist well beyond the duration of this crisis, a precedent evident in Listed Investment Companies (LICs) focussed on equities.
Figure 1: Average product performance, March-April 2020
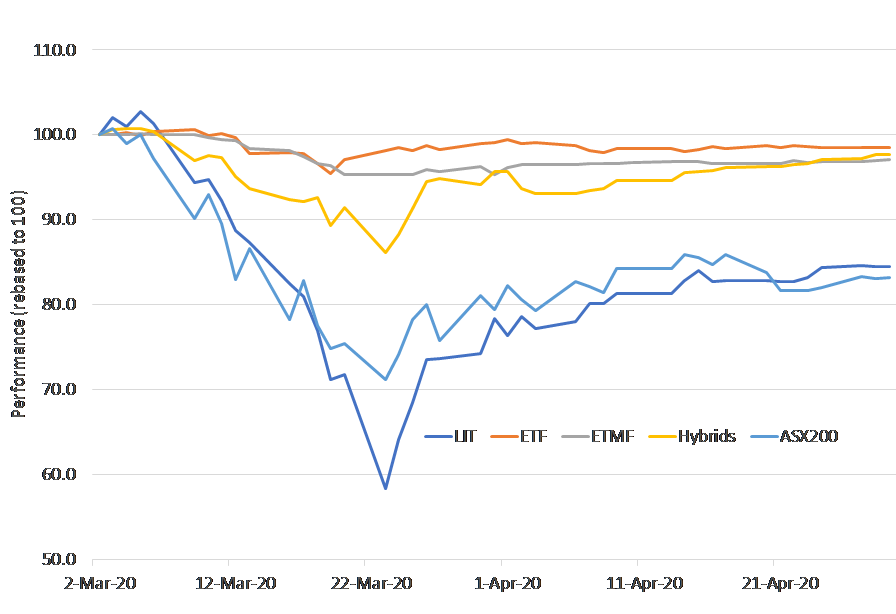
Source: Bloomberg, company websites. Following are ASX/Chi-X codes - LIT constituents: MXT, NBI, KKC, PGG, GCI. ETF constituents: IAF, VGF. ETMF constituents: ECOR, EMAX, XKAP, PAYS. Hybrids: HBRD.
Quality fixed income remains attractive
Current market conditions have created a real ‘stress test’ of investment options across all asset classes. Take residential property for example. Long seen as a stable option that offered a mix of income and capital growth, scores of investors are now facing the possibility of many months with little or reduced rent, reduced ability to evict troublesome tenants, and a difficult market for sales.
For income investors, the issue is a simple lack of diversification. While corporate bonds can become difficult to sell at times, a corporate bond portfolio provides significant diversification, protecting a continuing income stream even if one issuer runs into difficulties.
Investors with large allocations to liquid cash or government-guaranteed term deposits have contended with reinvestment risk for years now, and sadly continues to loom large. Even though consumer price inflation is expected to remain subdued for some time, falling returns and cash flow from deposit products is impacting a saver’s ability to meet their commitments.
Add to this the likely reduction in equity dividends in response to profit and economic contraction, and self-funded retirees are potentially facing several years of significant income deficiency. Corporate bonds, by comparison, have clearly-defined payment schedules, and the vast majority are mandatory payments that cannot be cancelled or varied without severe consequences for the issuer. After the volatility of recent months, yields on offer relative to deposit products are the highest for some time.
With the economic outlook still highly uncertain, the spreads of lower-rated bonds have (understandably) widened much more than investment grade debt. While it might be tempting to gravitate towards the higher yields on offer in some of these instruments, it is possible that we are only at the end of the beginning of this crisis, rather than on the cusp of a sustained recovery.
If this assessment is right, there is a strong case to tend toward investment grade securities. One key fact supporting this view is that observed defaults in higher-rated bonds are orders of magnitude lower than in the high yield market, a trend proven through countless market cycles. Avoiding defaults is the single most effective way to ensure success in fixed income investing.
Figure 2: Long-term defaults, IG and HY
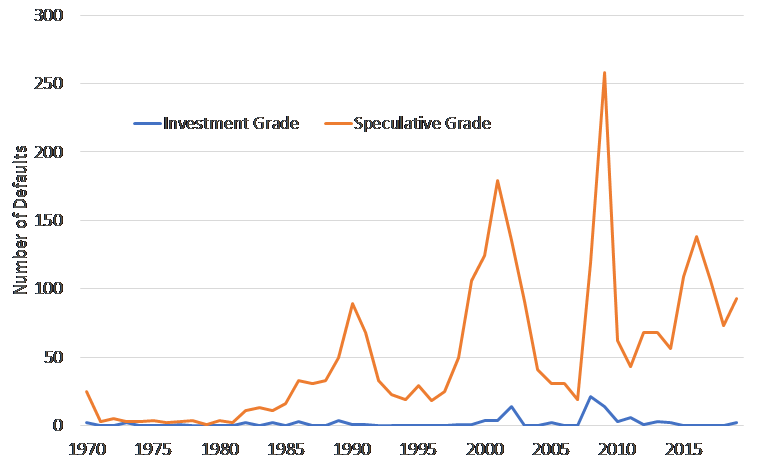
Source: Moody’s
Being nimble in fast-moving markets
Among the wide variety of fixed income offerings in the market, there has been considerable variability in outcomes for investors over March and April. Given the unprecedented and fluid nature of this crisis, it is difficult to establish any investment views with conviction.
While these uncertainties do extend to corporate credit as they do to all risk assets, this crisis is showing that not all fixed income instruments are created equally. With such an array of securities available in the market, additional work is not just necessary, but crucial to ensure that risks have been adequately weighed against the expected returns. Investors can increase their chances of success by exposure to well-diversified investment grade portfolios with a laser focus on liquidity and remaining nimble in the face of fast-moving markets.
Brad Dunn is a Senior Credit Analyst at Daintree Capital. This article contains general information only as it does not take into account the objectives, financial situation or needs of any particular person.