If you believe we are in a low-growth world, as we do, the attainability of real-return objectives will be difficult in an environment where bonds (and their proxies) are likely to be more challenged than equities. The response largely comes down to asset allocation.
In this article, we look at the part that cyclical volatility plays in achieving real returns, providing clues on how well-timed asset allocation can capture the upside of this cyclical volatility while attempting to avoid losses.
Cyclical considerations for decent returns
Cyclical volatility is normal in markets and can be significant in magnitude and can endure for relatively extended periods (three to five years in some cases). Returns are not linear. Even within structural ‘bear’ markets, significant rallies are likely. Investors who participate in the cyclical rallies but who can avoid the inevitable downswings can achieve decent returns. In contrast, in structural bull markets, cyclical volatility is less relevant as set and forget (i.e. beta alone) will deliver.
The critical question is can this cyclical volatility be managed and captured? It’s easier said than done.
This cyclical volatility is, in broad terms, driven by two interrelated factors: changes in valuations and the rotation of the business cycle. Our approach is to condition the long-run structural trend return in assets with shorter-run valuation dynamics to produce return forecasts over our investment horizon (three years), and to overlay this with an assessment of where we are in the cycle, and what this means for asset-price behaviour and policy. While by no means perfect, this provides a disciplined framework to buy when risk is low and sell when risk is high.
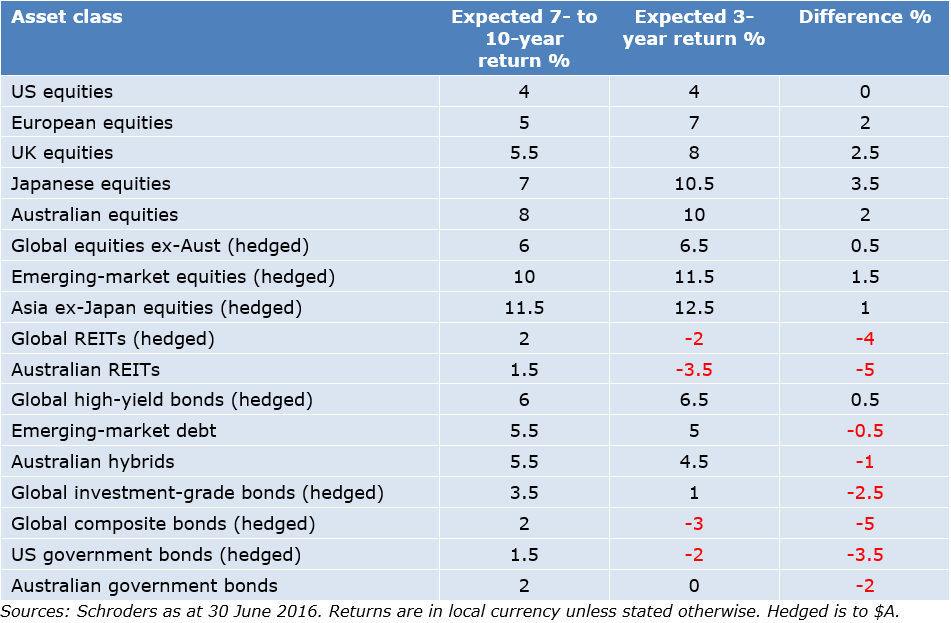
The key here clearly is the ability to capture the upswing but not ride the reverse. A summary of our cyclical (three-year) return forecasts is shown in the following chart and these are compared to our longer-run numbers.
It highlights that equity markets can be expected to deliver reasonable returns to investors over the next few years (albeit not necessarily in a linear fashion), whereas bond markets, and asset values that have been driven primarily from the decline in bond yields, could be expected to struggle or deliver negative returns. The numbers in the table exclude the impact of currency and active security selection, which over time we would expect to contribute to returns.
Expected three-year and longer-run returns
There are significant implications from an investment perspective:
1. Which market and when will be crucial: Market performance (beta) will be crucial in order to deliver real returns in coming years. Appropriate and potentially aggressive shifts in asset allocation will be essential to capturing upside, and more significantly, avoiding giving away gains as markets decline.
2. Sovereign bond outlook looks poor: Until appropriate risk premia in bond markets are restored and monetary policies move towards more normal settings (albeit probably a ‘new normal’), the sovereign bond outlook looks poor (at best). Equity markets are more likely to be significant contributors to returns (albeit will likely struggle if/when bond markets re-rate).
3. Assets structurally linked to declining bond yields are at risk: The most problematic assets are likely to be strategies where performance is structurally linked to the decline in bond yields. At an asset-class level, these include sovereign bonds, infrastructure and REITs.
4. Be cautious around structured/alternative betas and complex financial engineering: We remain cynical about alternatives, particularly when market pricing has been heavily distorted by central bank policies. Alternatives such as hedge funds have historically over-promised and under-delivered, particularly after fees. While it is logical in a world where returns from equities and bonds (the predominant market betas) are likely to be constrained, this path is unlikely to solve the low-return problem in the medium to longer term.
5. Leverage brings additional risk and may not solve the fundamental problem of low returns: Non-directional alpha strategies are for the most part relative value trades, requiring leverage, potentially bringing additional risk. The current environment is not one conducive to leverage. There’s also often more beta in these strategies than what appears on the surface.
6. Transparency, liquidity and the ability to hold cash will be important elements of a successful strategy: The implications of low bond yields on portfolio diversification may mean less aggregate equity positions, higher cash weightings than would be traditionally the case or more aggressive use of lower-risk equity substitutes.
7. Active asset allocation (in fact, active management generally) will be incredibly important. Capturing the upside of this cyclical volatility will be crucial, but more crucial will be avoiding the losses on the other side.
There is no doubt that achieving CPI+5% consistently will be tough. Investors will likely be episodically biased to equities over bonds, need to be aggressive in managing asset allocation around these trends, and use active management at the asset-class level to gain higher returns. The risk to delivering return objective consistently is to the downside.
Simon Doyle is Head of Fixed Income & Multi-Asset at Schroder Investment Management Australia Ltd. Opinions, estimates and projections in this article constitute the current judgement of the author. They do not necessarily reflect the opinions of any member of the Schroders Group. This document should not be relied on as containing any investment, accounting, legal or tax advice.