The Weekend Edition includes a market update plus Morningstar adds links to two additional articles.
Here we are in little Australia, down under with only 26 million people in a world of 8 billion (0.33%), ranked 55th among all countries by population, with a stock exchange worth less than 2% of global capitalisation. Travel overseas and you'll see we are almost ignored in the news cycle of major countries unless a shark bites someone, a bush fire ravages a town or Australia wins a sporting event. And with thousands of cities on the planet, this tiny country boasts three cities ranked as 'least affordable' housing markets in the Top 15 in the entire world - Sydney at 2, Melbourne at 9 and Adelaide at 14. Let's throw in Auckland at 7 for good measure.
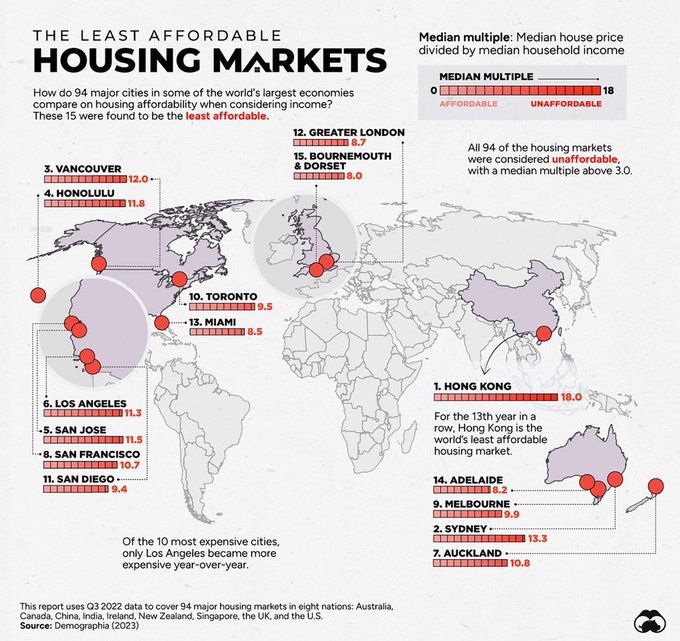 Source: Demographia
Source: Demographia
Everyone has their own lists of reasons. We have a culture of home ownership, where about two-thirds of Australian adults own their own home (and 80% over the age of 55), unlike say Switzerland which is closer to 40%. The tax system excludes the home from social security tests and capital gains tax, while short-term leases discourage renting. Residential leases of 10 and 20 years are common in Europe but the most frequent in Australia is a vulnerable one-year. Australian banks are eager to lend for home mortgages but less so for business loans, and many families accept they will need two incomes to service their debt while they struggle for child care. The Bank of Mum and Dad is common.
And then there's population growth, especially through immigration. It will become more of a political issue at the next election as more people cannot find rental properties and owners are increasingly priced out of market. There is a supply and demand imbalance, and many builders have gone into liquidation. The recovery in house prices in 2023 has defied most economists who were expecting a fall, some as high as 30% from the 2022 highs.
 Source: CoreLogic
Source: CoreLogic
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) Media Release entitled 'Overseas migration drives Australia's population growth' on 14 September 2023, the population grew by 2.2% to 26.5 million people in the 12 months to 31 March 2023. Head of Demography, Beidar Cho, said:
“13 months after international borders were re-opened, net overseas migration accounted for 81% of growth and added 454,400 people to the population in the year to March 2023.”
The ABS reported that net overseas migration was driven by a large increase in arrivals (up 103% from last year to 681,000) and only a small increase in overseas migrant departures (up 8.8% to 226,600). Natural increase was 108,800 people, a decrease of 18.5% from last year. Based on even later data, net immigration will top over 500,000 in the 2022/23 financial year making the housing shortfall even worse. It's the main reason economists are predicting further price rises despite higher interest rates.
 Source: AMP/Shane Oliver
Source: AMP/Shane Oliver
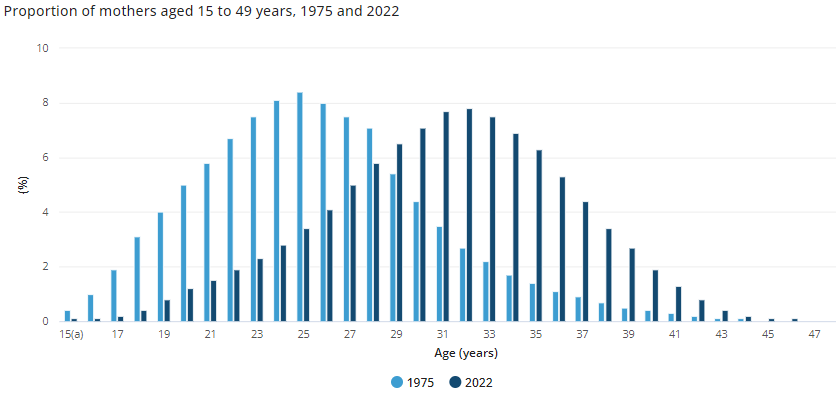
The dramatic shift in birth statistics also released by the ABS shows demographics can change in a couple of generations. This chart shows the age of mothers having children in 2022 peaks at 32 years versus 25 years in 1975. As my wife said, imagine how old the grandparents and great-grandparents will be.
The new Reserve Bank Governor, Michele Bullock, at the Australian Financial Security Authority’s annual forum, highlighted the house price recovery despite the tightening of monetary policy. Here are a few points she made:
"Actually, the housing market has surprised me a bit. So, if you remember the history, when COVID first hit, housing prices actually declined and then, after a few months, they shot up, and they shot up about 20, 25%; they really rose very, very sharply. Then, when interest rates started to rise, housing prices started to decline, and we thought that they would continue to decline, this is of the existing housing stock, if you like. But, actually, they bottomed sooner than we thought and, basically, now they’re back to where they were in their peaks of the pandemic.
Now, there’s a few things going on here, I think. One is that, as you alluded to, there’s difficulties in the construction of new housing at the moment. There’s a pipeline there; there’s an unfinished pipeline of housing stock, detached housing stock, which because of supply chain issues, inflation in construction costs, shortages of labour, particularly subcontractors, that isn’t being finished. And so the cost of new housing has risen quite sharply and that, I think, has made the equation between ‘build a new house’ or ‘buy an existing house’ change, somewhat. The other thing that’s happened is rents have risen a lot, and that’s that the supply of housing isn’t meeting the demands for housing."
A recent study by the University of Adelaide and University of Essex found that renting leads to faster ageing, including:
“Our findings demonstrate that housing circumstances have a significant impact on biological ageing, even more so than other important social determinants, such as unemployment, for example, and therefore health impacts should be an important consideration shaping housing policies.”
Housing is such a significant policy and political issue in Australia that financial legislation including superannuation and retirement should be framed in some way by the implications for home ownership.
***
Some fascinating tussles in bond markets at the moment, both locally and in the biggest market of all, the US. The Australian Government issued $8 billion of June 2054 bonds at a yield of 4.93% after receiving $29 billion of bids. Despite the long duration and risk, there are plenty of investors snapping up the near-5% yield which looked highly unlikely in recent years. The Australian Office of Financial Management provided a report on their issuing activity but a glance at the chart below shows how much cheaper it would have been if they had jumped on the rates of 2020.

Action in the bellwether 10-year US Treasury was also lively this week as it briefly exceeded 5% but has since settled back to around 4.9%. US investor, Bill Ackman, gained more publicity and notoriety by covering his bond short (buying bonds) two months after publicly taking a big bet that rates would continue rising. Here is the reaction in the following few hours, and he enjoyed it, showing how quickly the rally went from 5% to 4.85%.

***
Lots of discussion on the proposed new $3 million tax on superannuation, with most of it now centred on taxing unrealised gains. Some useful alternatives are surfacing which Treasury ought to consider. In Firstlinks last week, this example from a reader, 'Tasman', shows how an SMSF trustee could be severely affected:
"The proposed tax should make anyone considering buying into high risk, growth stocks (exploration ,biotech, technology) tread carefully, maybe reconsider. A biotech our SMSF holds has gone from 1.6c (2019) to 60.5c (2021) to 4.1c (today). A disaster if the new tax had been applied."
Another call out, after Meg Heffron expressed her frustration at the $3 million tax being referred to as a 30% tax, not only by the media but by Treasury itself. Journalists continue to swoon over Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), now reaching $150 billion, such as The Australian Financial Review leading with its article, 'Why everyone is investing in ETFs' including describing ETFs as the 'biggest investment trend of the decade". The total amount in ETFs is about half the funds managed by AustralianSuper alone, and the total amount in managed funds is $4.6 trillion, according to the ABS. Which puts ETFs at about 3% of managed funds. No, while ETFs are growing, the majority of Australians are not investing in them.
Graham Hand
In this week’s edition...
It’s been dubbed ‘The Great Wealth Transfer’, where Baby Boomers are expected to pass on around $3.5 trillion in assets to their children over the next two decades. A new report by Fidelity International suggests Australians are keen to share their wealth with the next generation but are unsure about the best ways to go about it, as James Gruber reports.
For much of the past decade, retirees had to deal with issues of low deposit rates on their savings. Since the end of Covid, a new threat has emerged: inflation. By constantly eating away at the value of savings and income, inflation can slowly reduce purchasing power in retirement. Bob French at Retirement Researcher has tips on how to inflation-proof your retirement portfolio.
Meanwhile, it’s well known that any money withdrawn from superannuation after age 60 is tax-free. Less well known is the arrangement that allows a couple over the age of 67 to earn up to $57,948 per year outside super and pay no tax. Jon Kalkman has the details.
ASX blue-chip stock ResMed is down almost 40% in less than five months due to concerns that new obesity drugs will reduce demand for its products. Vinay Ranjan from Airlie Funds Management explains what these drugs are, their effectiveness, and the potential impact they could have on the sleep apnoea market.
Over 10 years of surveying large super funds and the portfolio managers and consultants who help them to invest, Frontier Advisors' Wayne Sullivan notes that significant changes include the move to in-house investment staff, a change in the major decision-makers, fee competition and the top worries.
Bonds have been crushed over the past two years, yet equities have held up reasonably well. Clime’s John Abernethy thinks a reversal in fortunes is probable over the next 12 months. However, he still believes equities are a better place to invest over a longer timeframe.
The assets which have performed well lately have notably come from outside traditional asset classes, such as Bitcoin and gold. Gold is near Australian dollar all-time highs thanks in part to rising tensions in the Middle East. Should gold be part of your investment portfolio, and if so, how much? The World Gold Council's Jaspar Crawley offers his thoughts.
Two extra articles from Morningstar for the weekend. Mark LaMonica looks at 11 ASX stocks offering great value right now, while Adam Fleck says be careful of the ESG risks in these 8 US-based AI companies.
And in this week's White Paper, we've gone for something different: two short videos from Magellan on AI and opportunities from the energy transition.
***
Weekend market update
On Friday in the US, after opening decisively higher on a surge in Amazon as well as Intel, news that Israel is moving closer to a ground invasion of Gaza knocked the wind out of Wall Street. The S&P 500 finished 0.5% lower, the Dow fell 1.1%, while the Nasdaq rose 0.4% thanks largely to Amazon. The S&P 500 is now 10.3% off its July peak. Meanwhle, Treasurys painted a mixed picture with the long bond rising two basis points to 5.03% and the two-year settling at 4.99% from 5.02% a day ago. Gold topped US$2,000 an ounce for the first time since May, WTI crude jumped above US$85 a barrel and the VIX settled north of 21.
From AAP Netdesk:
The local share market on Friday finished slightly higher but the gains did not come close to keeping it out of the red for the week, with a third-straight monthly decline looming. The benchmark S&P/ASX200 index on Friday closed up 14.6 points, or 0.21%, to 6,826.9. The broader All Ordinaries gained 13.1 points, or 0.19%, to 7,014.2. For the week the ASX200 lost 1.1% - its fifth week of losses out of the past six - pressured by higher bond yields, rising interest rate expectations and fears of the war in Gaza becoming a broader Middle Eastern conflict. The index closed at a one-year low on Thursday and is down 3.2% for the month, with two trading sessions left in October.
Six of the ASX's 11 sectors finished higher on Friday and five closed lower.
Consumer staples were the biggest mover, climbing 1.3% as Coles added 2.1% and Endeavour Group rose 3.5%.
All the big banks closed higher, with NAB adding 0.7% to $28.40, CBA gaining 0.8% to $97.80, Westpac climbing 0.5% to $20.67, and ANZ finishing up 0.2% at $24.85.
Insurance companies were lower as broker network Steadfast gave what appeared to be a positive quarterly update at its annual general meeting.
Steadfast dropped 4.3% to an eight-month low of $5.35, while Medibank Private fell 2.9%, IAG dropped 1.9% and QBE dipped 1.7%.
The heavyweight mining sector rose 0.6%, bolstered by China's announcement of additional fiscal stimulus measures. BHP gained 0.3% to $45.06, Fortescue rose 0.2% to $22.25 and South32 added 2.8% to $3.33.
Newmont Corp made its debut on the ASX after the world's biggest goldminer completed its acquisition of Newcrest. The Newmont CDIs finished at $59.50 under the ticker code NEM.
Brambles fell 5.7% to a seven-month low of $13.19 as the global pallet company reconfirmed guidance and announced first-quarter sales growth of 13%, but added that new business wins had been modest.
Harvey Norman grew 4.8 per cent to a 10-day high of $3.72 as the white goods and home retailer announced a $442.3 million share buyback. It also said that sales had dropped 9.1% in September quarter, with Australian sales down 13.6%.
ResMed dropped 4% to $21.56 after the respiratory product device-maker said that margins fell in the first quarter due to a battery issue with its Astral ventilators.
From Shane Oliver, AMP:
Most global share markets fell again over the last week on the back of ongoing worries about high bond yields, the war in Israel and some mixed US earnings results. For the week US shares fell 2.5%, Eurozone shares fell 0.3% and Japanese shares lost 0.9%. However, Chinese shares rose 1.5% helped by the announcement of policy stimulus. The poor global lead along with increased expectations for another rate rise following hawkish RBA comments and higher than expected inflation data saw the Australian share market fall another 1.1% for the week taking it back to levels last seen a year ago with falls led by property, IT and energy shares. 10-year bond yields pulled back a bit in the US and Europe but rose further in Japan and Australia. Oil prices fell, despite a rise later in the week on the back of reports of expanding Israeli military activity in Gaza. Metal and iron ore prices rose with the gold price rising back above $US2000 for the fourth time in the last few years. The $A rose slightly, despite a rise in the $US.
In Australia another rate hike is now looking likely after September quarter inflation came in higher than expected at 5.4%yoy. The good news is that inflation is falling, down from 6% in the June quarter and 7.8% in the December quarter. This is consistent with the global trend and we are continuing to see slowing inflation in food, clothing, new dwelling purchase costs and household equipment & furnishings helped by slowing goods price inflation. Holiday travel inflation also continues to slow.
…but the bad news is that inflation fell less than expected and particularly less than the RBA had been expecting. The trimmed mean underlying measure only slowed to 5.2%yoy which is significantly above the RBA’s forecast in August that it would slow to around 4.8%yoy (as implied by a graph in its Statement on Monetary Policy). And beyond the 7.2% surge in petrol prices and the 4.2% rise in electricity prices, services inflation remains sticky evident in strong increases in rents, meals & takeaway, vet services, hairdressing and insurance. The breadth of price increases also increased slightly with a rise to 59% of components seeing a more than 3% annualised price rise.
Curated by James Gruber and Leisa Bell
Latest updates
PDF version of Firstlinks Newsletter
nabtrade Charity Trading Day, 31 October 2023, partnering with Good Shepherd.
ASX Listed Bond and Hybrid rate sheet from NAB/nabtrade
Listed Investment Company (LIC) Indicative NTA Report from Bell Potter
LIC Monthly Report from Morningstar
Plus updates and announcements on the Sponsor Noticeboard on our website